Jul 15 2008
Cymbals don't clash of their own accord - in our world, anyway.
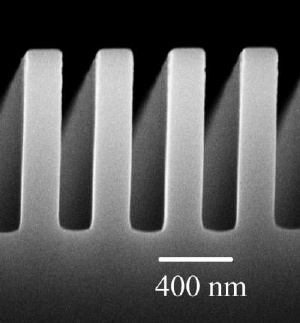 A scanning electron micrograph, taken with an electron microscope, shows the comb-like structure of a metal plate at the center of newly published University of Florida research on quantum physics. UF physicists found that corrugating the plate reduced the Casimir force, a quantum force that draws together very close objects. The discovery could prove useful as tiny “microelectromechanical” systems -- so-called MEMS devices that are already used in a wide array of consumer products -- become so small they are affected by quantum forces.
A scanning electron micrograph, taken with an electron microscope, shows the comb-like structure of a metal plate at the center of newly published University of Florida research on quantum physics. UF physicists found that corrugating the plate reduced the Casimir force, a quantum force that draws together very close objects. The discovery could prove useful as tiny “microelectromechanical” systems -- so-called MEMS devices that are already used in a wide array of consumer products -- become so small they are affected by quantum forces.
But the quantum world is bizarrely different. Two metal plates, placed almost
infinitesimally close together, spontaneously attract each other.
What seems like magic is known as the Casimir force, and it has been well-documented
in experiments. The cause goes to the heart of quantum physics: Seemingly empty
space is not actually empty but contains virtual particles associated with fluctuating
electromagnetic fields. These particles push the plates from both the inside
and the outside. However, only virtual particles of shorter wavelengths —
in the quantum world, particles exist simultaneously as waves — can fit
into the space between the plates, so that the outward pressure is slightly
smaller than the inward pressure. The result is the plates are forced together.
Now, University of Florida
physicists have found they can reduce the Casimir force by altering the surface
of the plates. The discovery could prove useful as tiny “microelectromechanical”
systems — so-called MEMS devices that are already used in a wide array
of consumer products — become so small they are affected by quantum forces.
“We are not talking about an immediate application,” says Ho Bun
Chan, an assistant professor of physics and the first author of a paper on the
findings that appears today in the online edition of the journal Physical Review
Letters.
“We are talking about, if the devices continue to be smaller and smaller,
as the trend of miniaturization occurs, then the quantum effects could come
into play.”
More specifically, the finding could one day help reduce what MEMS engineers
call “stiction” — when two very small, very close objects
tend to stick together.
Although stiction has many causes — including, for example, the presence
of water molecules that tend to clump together — the Casimir force can
contribute. Such quantum effects could prove important as the separations between
components in tiny machinery shrink from micrometer, or millionths of a meter,
toward nanometer size, Chan said.
“A lot of people are thinking of ways to reduce stiction, and this research
opens up one possibility,” he said.
Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir first predicted that two closely spaced metal
plates would be mutually attracted in 1948. It took several decades, but in
1996, physicist Steve Lamoreaux, then at the University of Washington, performed
the first accurate measurement of the Casimir force using a torsional pendulum,
an instrument for measuring very weak forces.
Subsequently, in a paper published in Science in 2001, Chan and other members
of a Bell Labs team reported tapping the Casimir force to move a tiny metal
see-saw. The researchers suspended a metal sphere an extremely tiny but well-controlled
distance above the see-saw to “push” it up and down. It was the
first demonstration of the Casimir force affecting a micromechanical device.
In the latest research, the physicists radically altered the shape of the metal
plates, corrugating them into evenly spaced trenches so that they resembled
a kind of three-dimensional comb. They then compared the Casimir forces generated
by these corrugated objects with those generated by standard plates, all also
against a metal sphere.
The result? “The force is smaller for the corrugated object but not as
small as we anticipated,” Chan said, adding that if corrugating the metal
reduced its total area by half, the Casimir force was reduced by only 30 to
40 percent.
Chan said the experiment shows that it is not possible to simply add the force
on the constituent solid parts of the plate — in this case, the tines
— to arrive at the total force. Rather, he said, “the force actually
depends on the geometry of the object.”
“Until now, no significant or nontrivial corrections to the Casimir force
due to boundary conditions have been observed experimentally,” wrote Lamoreaux,
now at Yale University, in a commentary accompanying publication of the paper.
Besides Chan, the other authors of the paper are UF doctoral students Yiliang
Bao and Jie Zou, and Bell Labs scientists Raymond Cirelli, Fred Klemens, William
Mansfield and Chien-Shing Pai. The research was funded by the U.S. Department
of Energy.