Liposomes are vesicles in which an aqueous volume is entirely enclosed by a membrane composed of lipid molecules, usually phospholipid. They can be prepared so that they entrap materials both within their aqueous compartment (water-soluble materials) and within the membrane (oil-soluble materials). They are extensively used as vehicles for the targeted delivery of drugs. The fate of intravenously injected liposomes is determined by a number of properties. Two of the most important are particle size and zeta potential.
Determination of Zeta Potential and Particle Size
The zeta potential is the overall charge a particle acquires in a particular medium. Both size and zeta potential can be measured on a Zetasizer 3000HSA.
The Importance of Zeta Potential to Liposomes
Knowledge of the zeta potential of a liposome preparation can help to predict the fate of the liposomes in vivo. Any subsequent modification of the liposome surface can also be monitored by measurement of the zeta potential.
Uptake of Liposomes by the Body
A major problem in the use of liposomes for the delivery of drugs by injection into the blood stream is the specific uptake of the liposomes by the reticuloendothelial system (RES). Longer circulation times can be achieved by coating the liposomes with a suitable polymer. Liposomes that lengthen circulation times in the blood and avoid uptake by the RES are called Stealth liposomes (Stealth is a registered trademark of Liposome Technology Inc., Menlo Park, CA).
The Effect Hydrophilic Polymers on Liposomes
The presence of hydrophilic polymers on the surface of the liposomes gives rise to a steric barrier which inhibits the adsorption of blood components which assist in the uptake of the liposomes by the RES.
The most successful hydrophilic polymers to date are polyethylene glycols (PEG). Figure 1 is schematic showing a liposome with covalently attached polyethylene glycol on the surface.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a polymer coated liposome.
Case Study – Zeta Potential Study of The Effect of Polyethylene Glycol on Liposomes
This application note describes zeta potential measurements of liposomes with polyethylene glycol covalently attached onto the surface.
Experimental
Anionic liposomes were prepared which contained a polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatized phospholipid at different concentrations.The polyethylene glycol had a molecular weight of 2000 Daltons. The zeta potentials of these liposome preparations were measured using a Malvern Panalytical Zetasizer 3000HSA in saline at physiological concentration.
Results
Figure 2 shows a plot of the measured zeta potential of liposomes as a function of the concentration of PEG derivatized phospholipid (mole %). The zeta potential of ‘naked’ liposomes (with no PEG present on the liposome surface) is –43mV.The zeta potential starts to decrease with increasing concentration of PEG derivatized phospholipid and eventually reaches a plateau around –5mV. The decrease in the zeta potential as the surface of the liposome is covered can be explained in one of two ways:
- The slipping plane being moved further away from the liposome surface and hence reducing the zeta potential,
- The drag caused by the presence of the PEG chains on the liposome surface reducing the mobility of the liposomes (and hence the zeta potential).
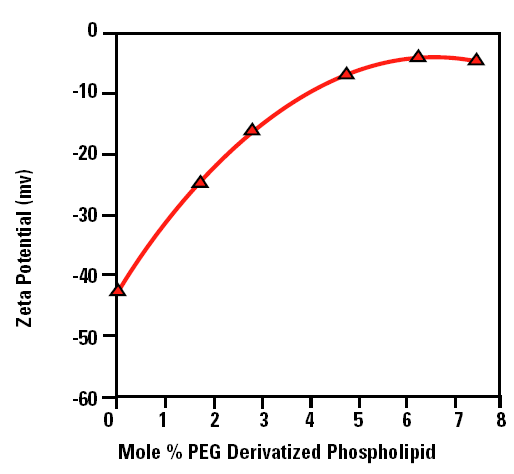
Figure 2. The zeta potential as a function of the mole % PEG derivatized phospholipid liposomes in saline at physiological concentration.
The plateau region observed in figure 2 corresponds to the point at which no more PEG molecules can fit around the surface of the liposome. In the data shown in figure 2, this point occurs at a concentration of 5 mole % of PEG derivatized phospholipid.
The measurements also show that samples in physiological strength saline can be easily measured in the Malvern Panalytical Zetasizer 3000HSA.
Conclusions
The surface characteristics of steric stabilised liposomes are determined by both the molecular mass of the PEG and the amount of the PEG derivatized phospholipid incorporated into the lipid bilayer. Such surface characteristics of liposomes can be investigated by measurement of the zeta potential.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Malvern Panalytical.
For more information please visit Malvern Panalytical.