Murphy’s Law predicts that it takes the first 99% of your time budget to finish the first 99% of a job and the second 99% to get it completed. The history of piezoelectric motors can serve as a good example here. After figuring out the relatively simple basic principles of piezoelectric motors, in the early 20th century, it still took design and manufacturing engineers a few more decades to move beyond the prototype and lab example state to a reliable, industrial product. Over the years, many different types of piezo motors which work quite differently from electromagnetic motors have been developed and tested.
Today, piezo motors have become major driving elements in commercial and industrial applications. Compared to traditional electric motors, it took much longer and more effort to reach to this point. This was because of the precision needed for mechanical parts as well as in the complexity of the drive electronics, which only became available with the abundance of high-powered digital chips at affordable costs.
Piezo Motors
All piezo motors produce motion depending on minute deformation of a piezoceramic material induced by a change in the applied electric field. There are several rotary and linear principles based on slow or high-frequency oscillatory motions. Generally, there are three types of piezo motors: Piezo-walk drives, inertia-motors (stick-slip principle) and resonance-motors (ultrasonic drives).
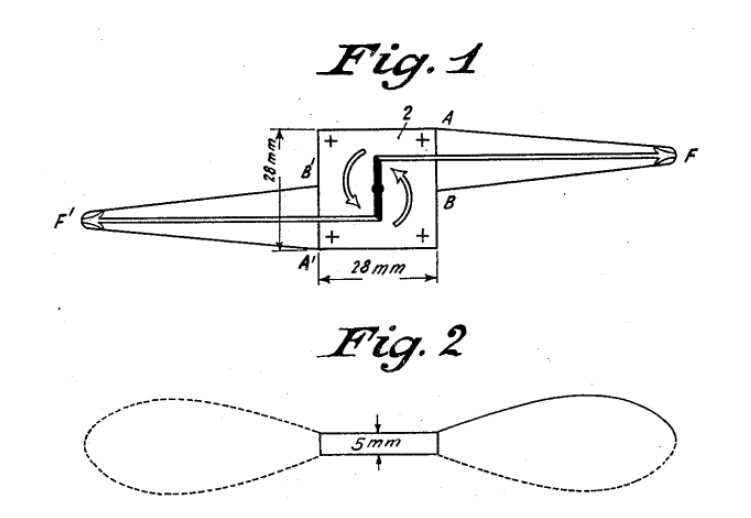
Piezoelectric oscillating element to obtain mechanical movement as described in an early US Patent by Meissner, US Patent 1,804,838 A, 12 May 1931.
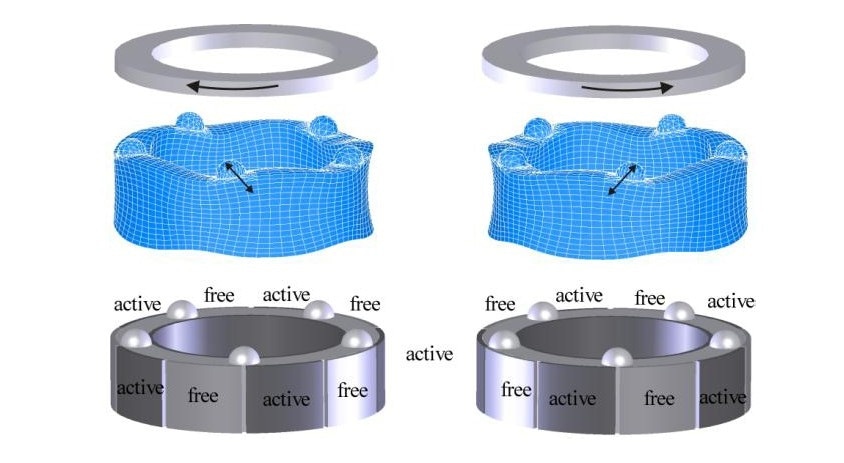
PI Closed-Loop Rotary Tables: How Ultrasonic Transducers in Direct Drive Miniature Rotation Stages
Operating principle of an ultrasonic single mode excitation resonance motor, using a cylindrical piezoelectric element (Image PI).
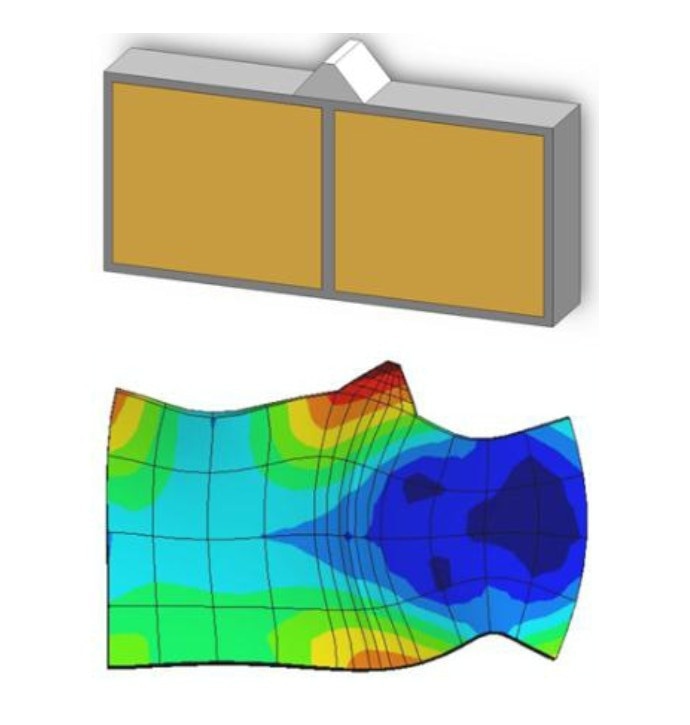
Precision Motion Control w/ Ultrasonic Piezo Motors: - Closed-Loop Linear Stages, Rotary Stages | PI
Single-mode excitation type ultrasonic piezo motor from Physik Instrumente (PI). The excited single mode of the stator makes the pushing point to have a sloping impact to a sliding element.
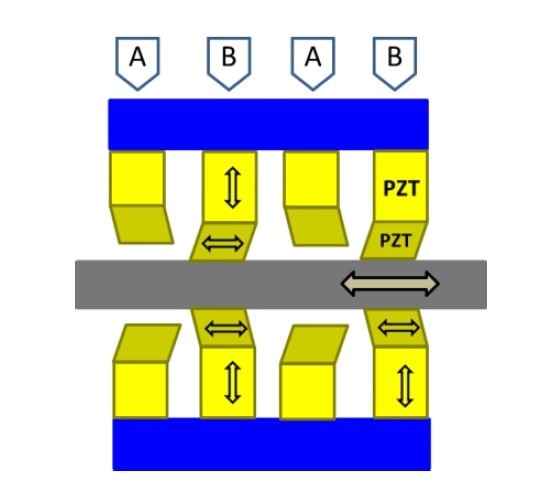
What is a Piezo Motor? How does it work? Piezo Motor Designs for Automation & Motion Control | PI
A Piezo-Walk linear piezo motor. This type of motor combines high forces with sub-nanometric resolution. (Image PI).
Stick / Slip Piezo Linear Motor Animation - Mini Motor Actuator by www.pi.ws
Mini-Rod stick-slip motor: These inertia drives are used in compact linear actuators, such as the N-412 and N-422 drives.
Closed-Loop Precision Actuators - How does a Piezo Ratchet Mechanism Work?
Piezo ratchet drives are a special form of inertia motors based on the stick-slip effect. A small piezo ceramic actuator embedded in a precision mechanism drives a high resolution screw. The drive principle relies on a quasi-saw tooth signal with a slow expansion phase and a fast contraction phase. This expansion leads to a small rotation of a high resolution lead screw. When the piezo element has reached its maximum expansion, a much shorter contraction phase follows – too fast for the screw to follow, because of its inertia.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co KG - Worldwide.
For more information on this source, please visit Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co KG - Worldwide.