Sponsored by Xenocs SASReviewed by Louis CastelOct 17 2022
Nanoparticles (NPs) are a fundamental building block for the creation of new materials with improved optical, mechanical or thermal properties.1
To meet performance, cost and safety requirements, parameters such as particle shape, size and concentration must be carefully controlled. An established method for traceable size measurements is Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS).2,3,4
It has recently been demonstrated that number concentrations of NPs can be accurately estimated from SAXS data acquired from synchrotron facilities with metrological traceability to the standard system of units (SI).5 This article demonstrates that traceable number concentrations can also be acquired using a SAXS laboratory setup with acquisition times of 10 minutes.
Measurements
A certified LGC concentration standard (colloidal dispersions of citrate-stabilized gold NPs, number concentration 1.47E11 ± 2.8E10 particles per mL, modal diameter 30.7 nm, product code LGCQC5050)6 has been measured both as-received and in dilution series.
The measurements were performed using a Nano-inXider instrument in a flowcell, and the thickness was identified by the transmission value.
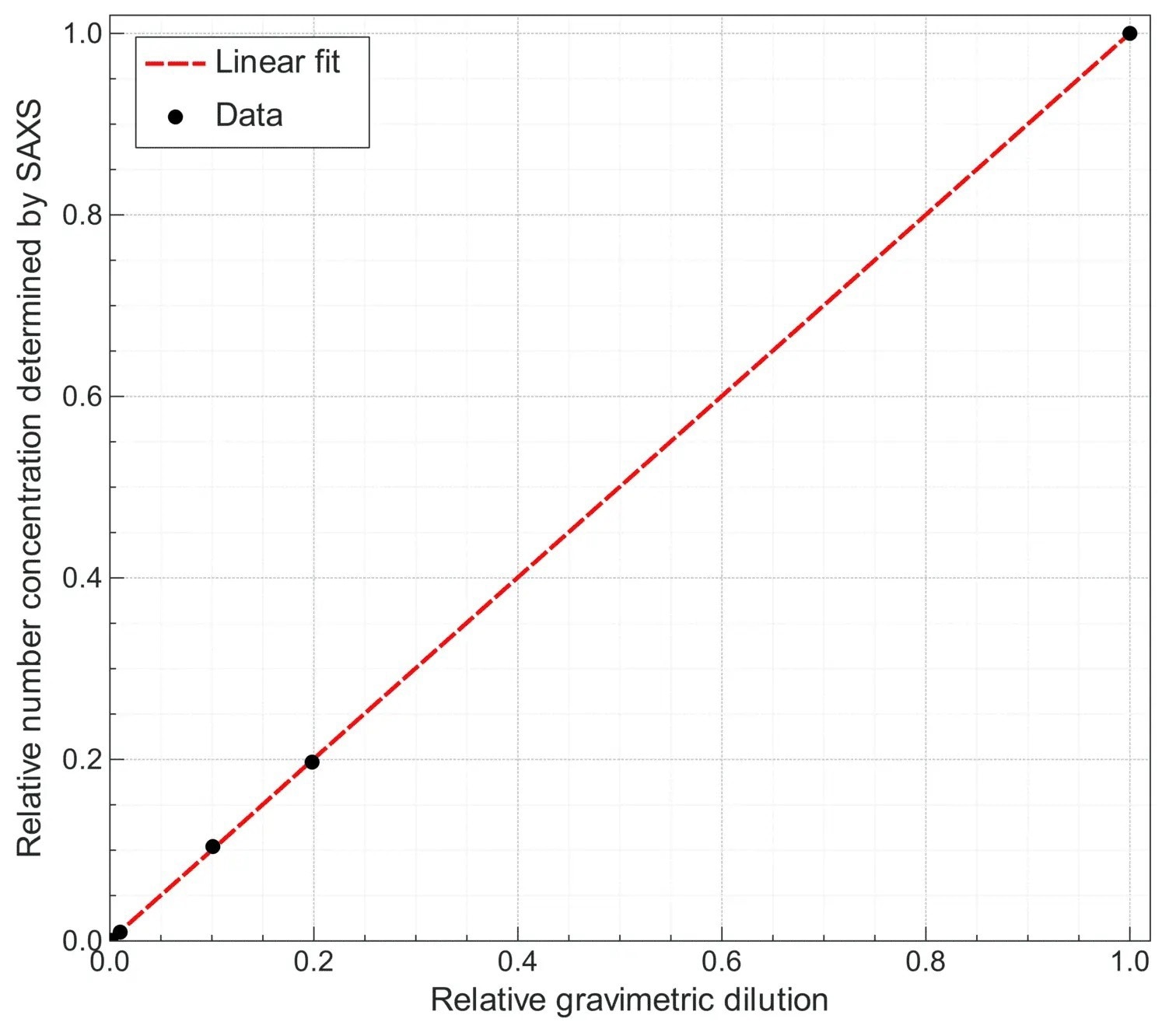
Figure 1. Colloidal dispersion of gold NPs with certified concentration measured as received and in dilution series. Relative number concentration obtained from the SAXS profile as a function of the relative dilution determined gravimetrically when preparing the dilution. Image Credit: Xenocs
Click here to gain access to the complete application note
References
- S. Logothetidis, Nanostructured Materials and Their Applications, Springer, 2012
- G. Gleber, L. Cibik, S. Haas, A. Hoell, P. Müller and M. Krumrey, “Traceable size determination of PMMA nanoparticles based on Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS),” Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 247, p. 012027, 2010
- F. Meli, T. Klain, E. Buhr, C. G. Frase, G. Gleber, M. Krumrey, A. Duta, S. Duta, V. Korpelainen and R. Bellotti, “Traceable size determination of nanoparticles, a comparison among European metrology institutes,” Measurement Science and Technology, vol. 23, p. 125005, 2012
- B. Pauw, C. Kästner and A. Thünemann, “Nanoparticle size distribution quantification: results of a small-angle X-ray scattering inter-laboratory comparison.,” Journal of Applied Crystallography, vol. 50, pp. 1280-1288, 2017
- A. Schavkan, C. Gollwitzer, R. Garcia-Diez, M. Krumrey, C. Minelli, D. Bartczak, S. Cuello-Nuñez, H. Goenaga-Infante, J. Rissler, E. Sjöström, G. B. Baur, K. Vasilatou and A. Shard, “Number Concentration of Gold Nanoparticles in Suspension: SAXS and spICPMS as Traceable Methods Compared to Laboratory Methods,” Nanomaterials, vol. 9, no. 4, p. 502, 2019

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Xenocs.
For more information on this source, please visit Xenocs.