Poly (propylene carbonate) is a solid polymer. It is an amorphous, clear, readily processible plastic with long term mechanical stability.
Technical Name Poly (propylene carbonate)
Chemical Formula (C4H6O3)n
Molecular Weight Available From approximately 100,000 to 300,000
Applications
- Binder applications for ceramics, metal or glass powders
- Pastes and inks
- Used to make high purity technical parts
- Coatings
- Sacrificial structural applications
- Decomposable channel former
- Pore former
- Non-binder applications for barrier film in plastic processing
Typical Physical Properties
| Property |
Value |
| Density (g/cm3) |
1.26 |
| Refractive Index |
1.463 |
| Decomposition Temperature (°C) |
250 (estimate) |
| Glass Transition Temperature (°C) |
15-40 |
| Heat of combustion (cal/gm) |
4,266 |
| Heat of formation (cal/mol) |
-146,000 |
| Molar Mass of repeating unit |
102.1 |
| Solubility |
Upon request |
Product Delivery Form It is available as a pellet, film, in solution form or as an aqueous emulsion
Benefits
- QPAC®40 leaves very little ash residue on decomposition: less than 10 ppm. This results in excellent mechanical and/or electrical properties
- Components made from QPAC®40 have excellent green strength resulting in final parts with high density and better structure
- Decomposition takes place at low temperature which is important for thermal sensitive materials and does so more efficiently than other binders
- Decomposition can take place in a wide range of atmospheres including oxygen, hydrogen, air, nitrogen, argon and vacuum
TGA for QPAC® 40
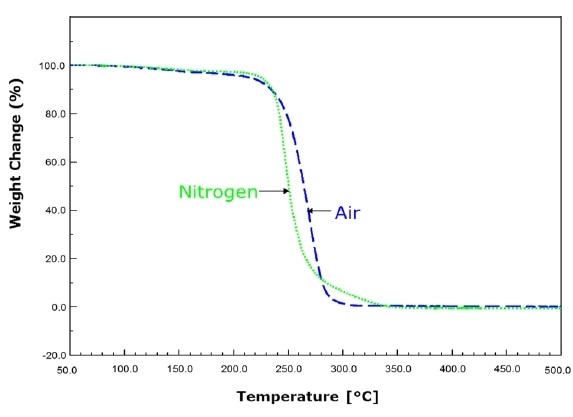
Image Credit: Empower Materials