North Carolina State University researchers have devised a novel technique for fabricating elastic conductors using carbon nanotubes, paving the way to mass-produce stretchable conductors for applications in a new generation of stretchable electronic devices.
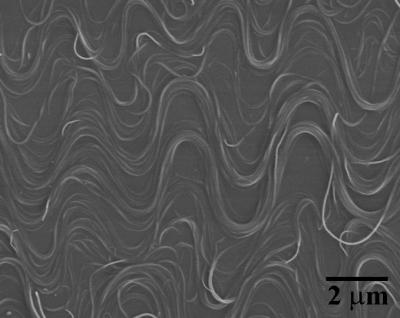 The buckled nanotubes look like squiggly lines on a flat surface. (credit: Yong Zhu, North Carolina State University)
The buckled nanotubes look like squiggly lines on a flat surface. (credit: Yong Zhu, North Carolina State University)
Elastic electronic devices have high resilience and are capable of conforming to different shapes. Potential applications are devices capable of being integrated into clothes, stretchable sensors for unmanned aerial vehicles and implantable medical devices.
Conductors used for fabricating elastic electronics must have elasticity and can transfer electric signals reliably even in the stretched state. In the new technique, the researchers utilized carbon nanotubes as they are stable, sturdy, superior conductors and capable of assembling into ribbons. They buckled the aligned nanomaterial on the surface of an elastic substrate utilizing transfer printing method. When the substrate is stretched, nanotubes get separated but continue their parallel alignment. Surprisingly, when the substrate is relaxed, the nanomaterials buckle to form a set of parallel squiggly lines over a plane surface rather than retaining their initial positions. The resulting carbon nanotubes are stretchable, yet have electrical properties.
The novel method can produce high-efficient elastic conductors, as it allows the carbon nanotubes to be applied prior to the substrate is stretched out. It is compatible with current production techniques such as roll-to-roll printing methods. The researchers reported their novel method in a paper titled ‘Buckling of Aligned Carbon Nanotubes as Stretchable Conductors: A New Manufacturing Strategy’ in Advanced Materials. In another paper, ‘Wavy Ribbons of Carbon Nanotubes for Stretchable Conductors,’ reported in Advanced Functional Materials, the researchers described the formation of a ribbon that resembles a set of parallel squiggly lines from carbon nanotubes.