Oct 10 2014
Some people might consider mucus an icky bodily secretion best left wrapped in a tissue, but to a group of researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, snot is an endlessly fascinating subject. The team has developed a way to use gold nanoparticles and light to measure the stickiness of the slimy substance that lines our airways. The new method could help doctors better monitor and treat lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
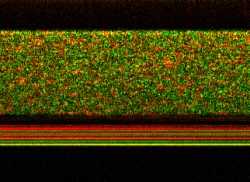 This image, captured by the UNC team, shows gold nanorods diffusing into a layer of mucus. The speckles in the top part of the image are due to rapid light intensity fluctuations caused by the gold nanorods as they move through the mucus. The black layer underneath is human lung cells, and the lack of green speckle shows that the nanorods have not penetrated the cells. The lines of solid color are the membrane. Credit: Amy Oldenburg, et al/UNC
This image, captured by the UNC team, shows gold nanorods diffusing into a layer of mucus. The speckles in the top part of the image are due to rapid light intensity fluctuations caused by the gold nanorods as they move through the mucus. The black layer underneath is human lung cells, and the lack of green speckle shows that the nanorods have not penetrated the cells. The lines of solid color are the membrane. Credit: Amy Oldenburg, et al/UNC
The research team will present their work at The Optical Society's (OSA) 98th Annual Meeting, Frontiers in Optics, being held Oct. 19-23 in Tucson, Arizona, USA.
"People who are suffering from certain lung diseases have thickened mucus," explained Amy Oldenburg, a physicist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill whose research focuses on biomedical imaging systems. "In healthy adults, hair-like cell appendages called cilia line the airways and pull mucus out of the lungs and into the throat. But if the mucus is too viscous it can become trapped in the lungs, making breathing more difficult and also failing to remove pathogens that can cause chronic infections."
Doctors can prescribe mucus-thinning drugs, but have no good way to monitor how the drugs affect the viscosity of mucus at various spots inside the body. This is where Oldenburg and her colleagues' work may help.
The researchers placed coated gold nanorods on the surface of mucus samples and then tracked the rods' diffusion into the mucus by illuminating the samples with laser light and analyzing the way the light bounced off the nanoparticles. The slower the nanorods diffused, the thicker the mucus. The team found this imaging method worked even when the mucus was sliding over a layer of cells—an important finding since mucus inside the human body is usually in motion.
"The ability to monitor how well mucus-thinning treatments are working in real-time may allow us to determine better treatments and tailor them for the individual," said Oldenburg.
It will likely take five to 10 more years before the team's mucus measuring method is tested on human patients, Oldenburg said. Gold is non-toxic, but for safety reasons the researchers would want to ensure that the gold nanorods would eventually be cleared from a patient's system.
"This is a great example of interdisciplinary work in which optical scientists can meet a specific need in the clinic," said Nozomi Nishimura, of Cornell University and one of the FiO subcommittee chairs. "As these types of optical technologies continue to make their way into medical practice, it will both expand the market for the technology as well as improve patient care."
The team is also working on several lines of ongoing study that will some day help bring their monitoring device to the clinic. They are developing delivery methods for the gold nanorods, studying how their imaging system might be adapted to enter a patient's airways, and further investigating how mucus flow properties differ throughout the body.