An overview of the range of useful applications of halloysite clay tubes has been published. The naturally occuring, biocompatible, nanoscale tubes can be used for sustained drug delivery and alongside enzymes as biocatalytic nanoreactors.
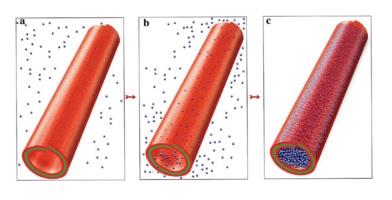 a) This image shows loading clay nanotubes with drug from saturation solution. b,c) Mixing with drug solution, pumping out air, and pulling in drug molecules, washing, and loaded tubes. (Credit: the author's of the article)
a) This image shows loading clay nanotubes with drug from saturation solution. b,c) Mixing with drug solution, pumping out air, and pulling in drug molecules, washing, and loaded tubes. (Credit: the author's of the article)
Halloysite is a naturally occuring, biocompatible, economical nanomaterial. These properties, alongside its high availability, makes halloysite a viable material for nano-architectural composites.
Halloysite has an extremely similar chemical compisiton to kaolin. Halloysite is literally a sheet of kaolin rolled into a tube with an outer diameter spanning between 40 and 70 nm, an inner diameter of 10 to 20 nm, and a length of 500 to 150 nm. The halloysite’s outer side is made up of SiO2 while its inner side is made up of Al2O3.
Etching the tube volume to 20-30% can adjust the inner lumen of halloysite, allowing it to be used as a natural nanocontainer for the sustained loading and release of chemical agents. These ceramic nanotubes take on a 'skeleton' shape in the bulk polymers; improving the strength and adhesivity of the composite.
It is possible to load these "skeleton bones" with active compounds, mimicing real bones that contain marrow. The loading of active components can be used to give polymers additional functionality such as anti-corrosion, flame retardancy, anti-microbial and anti-aging properties.
Enzymes can be encased within the halloysite tubes to increase their temperature stability and their storage lifetime, resulting in prolonged functionality. The opening of the tube allows for the release of small substrate molecules into the inside of the tube for biocatalysis.
Another potential area of research is the loading of DNA into the halloysite. Since halloysite tubes are functional nanoblocks, they can be applied in the construction of biological cells, such as the creation of spore-like microbial shells to provide additional functions to microorganisms.
The safety of halloysites was tested using in vitro and in vivo analyses performed on biological cells and worms.Since the halloysite is capable of storing and discharging molecules in a controllable manner, they are good potential candidates to be used in drug delivery, self-healing polymeric composites, antimicrobial materials and regenerative medicine.
However halloysites are not biodegradable. Also, it is not safe to intravenously inject halloysites into the blood. As a result, it is recommended only for external medical treatment where the slow release of encapsulated drugs is required such as in implants, creams or wound treatments.