Apr 11 2016
Our current understanding of how the brain works is very poor. The electrical signals travel around the brain and throughout the body, and the electrical properties of the biological tissues are studied using electrophysiology. For acquiring a large amplitude and a high quality of neuronal signals, intracellular recording is a powerful methodology compared to extracellular recording to measure the voltage or current across the cell membranes.
Nanowire- and nanotube-based devices have been developed for the intracellular recording applications to demonstrate the advantages of these devices having high spatial resolution and high sensitivity.
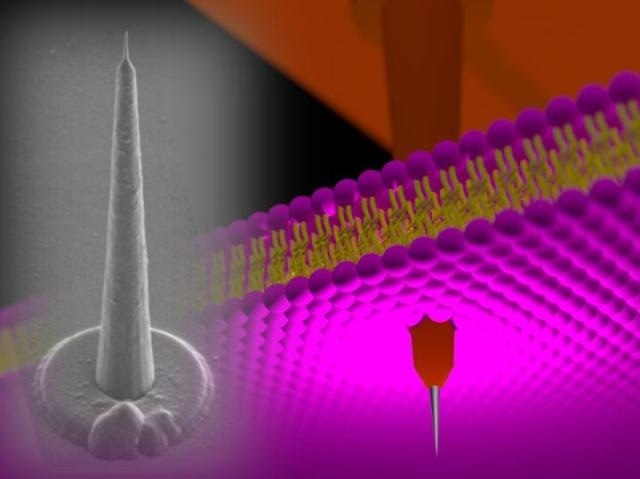 120-µm-height 'nanotower' electrode is punching a cell membrane. Silicon growth technology and three-dimensional nano/microfabrication techniques realize such high-aspect-ratio intracellular electrodes. (COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. )
120-µm-height 'nanotower' electrode is punching a cell membrane. Silicon growth technology and three-dimensional nano/microfabrication techniques realize such high-aspect-ratio intracellular electrodes. (COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. )
However, length of these nanowire/nanotube electrode devices is currently limited to less than 10 µm due to process issues that occur during fabrication of high-aspect-ratio nanoscale devices, which are more than 10-µm long. Thus, conventional nanodevices are not applicable to neurons/cells within thick biological tissues, including brain slices and brain in vivo.
A research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering and the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) at Toyohashi University of Technology has developed three-dimensional microneedle-based nanoscale-tipped electrodes (NTEs) that are longer than 100 µm. The needle length exceeds that of the conventional nanowire/nanotube-based intracellular devices, thus expanding the range of applications of nanodevices in intracellular recording, such as deep tissue penetration. Additionally, they perform intracellular recordings using muscle cells.
"A technological challenge in electrophysiology is intracellular recordings within a thick biological tissue. For example, a needle length of more than 40 µm is necessary for performing brain slice experiments. However, it is almost impossible to penetrate nanoscale diameter needles with a high-aspect-ratio, because of the long hair-like nanostructure that has insufficient stiffness. On the other hand, our NTE, which is 120-µm-long cone-shaped electrode, has sufficient stiffness to punch tissues and cells", explains the first author PhD candidate, Yoshihiro Kubota.
The leader of the research team, Associate Professor Takeshi Kawano said "Although we demonstrated the preliminary results of our NTE device, the batch fabrication of such intracellular electrodes, which have a needle length more than 100 µm, should lead to an advancement in the device technologies. This will eventually lead to realization of multisite, depth-intracellular recordings for biological tissues, including brain slices and brain in vivo, which are beyond the capability of conventional intracellular devices."
As addressed by the research team, the NTE has the potential to be used in cells that are deep within a biological tissue, including brain slice and brain in vivo, thus accelerating the understanding of the brain.