Jun 20 2019
How to enhance the flame-retardant performance of 2D flame retardants?
In a paper to be published in the next issue of NANO, a group of scientists from Henan University has studied the flame-retardant performance of epoxy resin with the help of a boron nitride nanosheet embedded with cobalt ferrite nanoparticle.
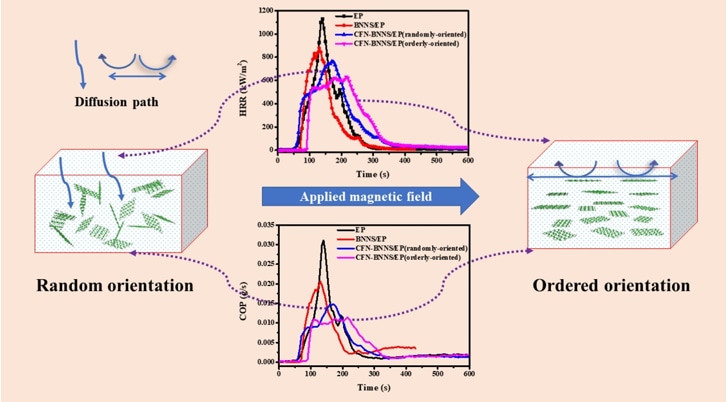 Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles decorated boron nitride nanosheets hybrid flame retardants were prepared through a simple solvothermal method. Subsequently, the orientation of the nanohybrids in epoxy resin was obtained under a rotating magnetic field. Due to enhancement of the barrier effect, the ordered alignment of the nanohybrids in epoxy resin contributes to better flame-retardant performance, compared with a random one. (Image credit: World Scientific)
Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles decorated boron nitride nanosheets hybrid flame retardants were prepared through a simple solvothermal method. Subsequently, the orientation of the nanohybrids in epoxy resin was obtained under a rotating magnetic field. Due to enhancement of the barrier effect, the ordered alignment of the nanohybrids in epoxy resin contributes to better flame-retardant performance, compared with a random one. (Image credit: World Scientific)
Polymers are extensively employed in day-to-day activities because of their corrosion resistance, excellent chemical and physical stability, and other outstanding properties. However, a majority of the polymers are innately flammable because of their organic nature, which poses a potential hazard to the safety of human life and property. Adding flame retardants to the polymers is an excellent approach to prevent or minimize the flammability of polymers.
Among them, 2D layered inorganic nanomaterials (nanosheets), represented by molybdenum disulfide, graphene oxide, and boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS), show exceptional flame-retardant performance because of their good physical barrier effects. However, the flame retardancy is not adequate in the use of such 2D inorganic flame retardants alone, specifically, the potential to curb harmful gases and smoke is weak.
In this research, the scientists employed cobalt ferrite nanoparticle (CFN) to adorn BNNS in order to acquire CFN-BNNS nanohybrids with excellent ability to decrease both the toxic hazard and heat hazard of epoxy resin (EP) composites, by utilizing CFN synergistic effect. More essentially, the as-prepared CFN-BNNS has better paramagnetic properties, thus housing the ordered orientation of BNNS in EP matrix under a weak magnetic field that can serve as a good physical barrier.
In comparison with a random one, the ordered orientation of the CFN-BNNS in EP offers superior flame-retardant performance. That is, the flame-retardant performance of the 2D flame retardants can be enhanced by the ordered arrangement under a weak magnetic field.
This technology offers a new method to enhance the flame-retardant performance of 2D flame retardants in thermoset polymer. This is the most important innovation. Moreover, it will help scientists design and synthesize more polymers with exceptional flame-retardant performance using this technique.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21371050) and the Program for Innovative Research Team from the University of Henan Province (grant No. 17IRTSTHN004).
Additional co-authors of the Nano paper include Dr Qiaoran Zhang, Prof. Xiaohong Li, Prof. Laigui Yu, Prof. Zhijun Zhang, and Prof. Zhishe Wu, from Henan University. The corresponding authors for this research include Zhiwei Li and Zhishen Wu.