An article from the journal Polymer Testing investigated and compared the qualities of several polymeric composites manufactured using 3D printing techniques, such as morphology and surface texture, mechanical performance, thermal characteristics.
Study: Nanoparticle Infused Plastic Products Fabricated By Machine Learning Guided 3D Printer. Image Credit: Pixel B/Shutterstock.com
Manufactured polymer components require a variety of qualities depending on their purpose, some of which may be supplied by employing polymeric filaments composed of multiple materials in varying quantities.
An Introduction to 3D Printing
A branch of additive manufacturing (AM) known as 3D printing is a cutting-edge technique that mixes materials to create products from three-dimensional model data.
As a consequence, this process produces relatively minimal waste. 3D printing technologies are presently used in a variety of applications, including mass manufacturing of various items, with use only increasing.
It is now feasible to make objects with complicated structures, lightweight materials, and customizable designs using this technology. Furthermore, 3D printing offers the advantages of efficiency, sustainability, versatility, and risk minimization.
One of the most important aspects of this technology involves choosing the correct parameters as they have a large impact on the product, such as its form, size, cooling rate, and thermal gradients. These qualities can then influence the evolution of the microstructure, its characteristics, and its deficiencies.
Machine learning could be used to establish the relationship between process conditions, microstructure, component shape, composition, flaws, and mechanical qualities for specific printed goods. These connections may aid in reducing the number of trials needed to produce high-quality outputs.
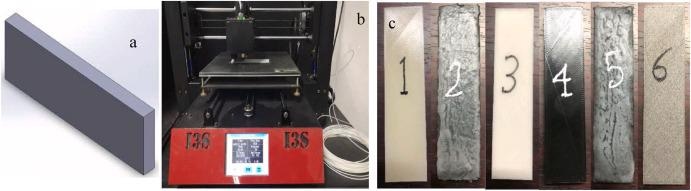
a. SolidWorks model, b. FFF 3D printer, c. printed specimens. Image Credit: Hossain, M. I. et al
Additive Manufacturing Materials
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) are the two most often utilized polymers in AM. PLA is employed as the primary material in several applications as it is sustainable, economically accessible, biodegradable, and has excellent features.
Plastic recycling is a major issue faced worldwide; thus, incorporating recyclable plastics into the process of 3D printing would be extremely advantageous.
While the printing material is continuously fed into a liquefier, the temperature is kept at a consistent level in fused filament fabrication (FFF) deposition, a type of 3D printing.
Consequently, the molten polymer is ejected via a nozzle by a decrease in pressure. Surface morphology, production output, geometrical accuracy, mechanical characteristics, and cost are all affected by FFF variables.
Tensile, compressive impact or flexural strengths, and printing orientation are regarded to be the most significant process variables affecting FFF samples. In this study, the FFF method was used to prepare specimens; six distinct filaments were employed to construct the specimen layers.
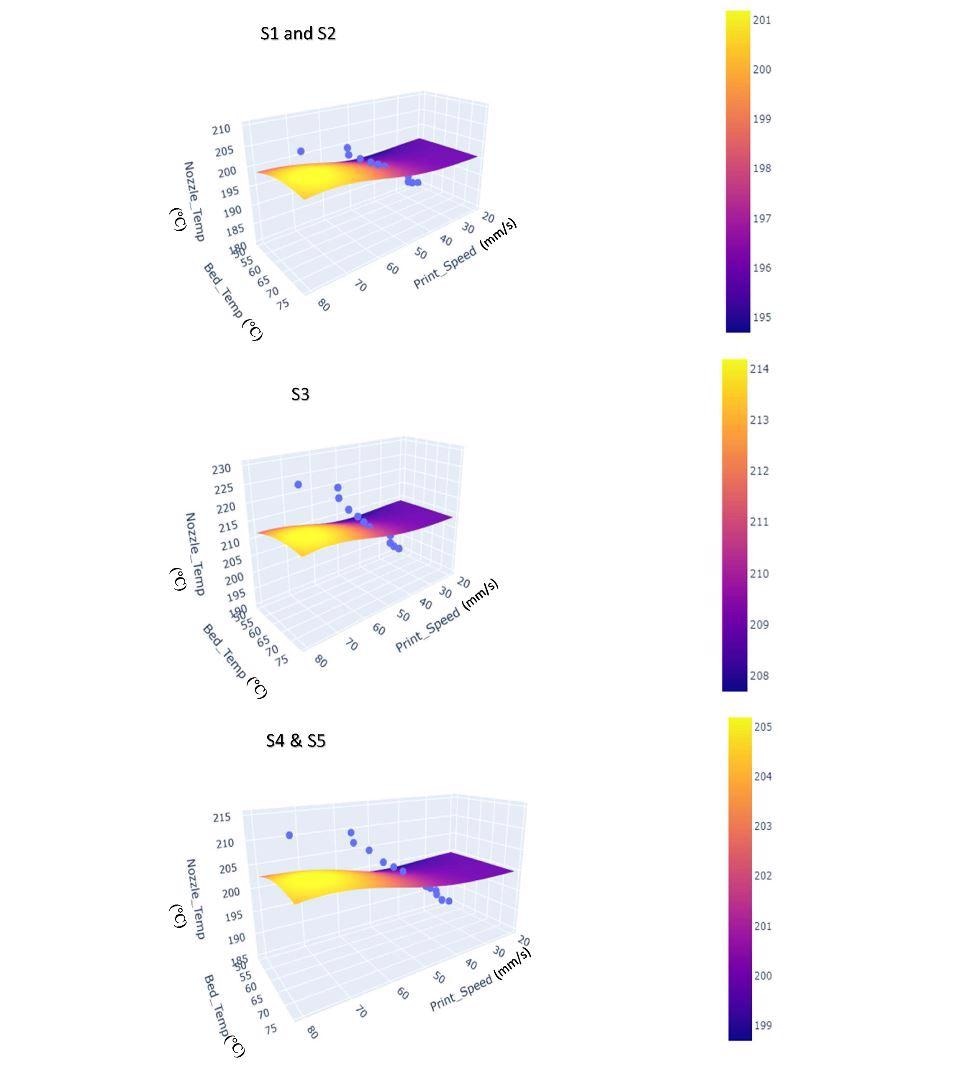
a: ML predicted parameter optimization model for 3D printer for sample 1 and 2, b: ML predicted parameter optimization model for 3D printer for sample 3, c: ML predicted parameter optimization model for 3D printer for sample 4 and 5. Image Credit: Hossain, M. I. et al
Role of Machine Learning
3D printing technology enables the combination of exceptional qualities for printed items that are otherwise impossible via traditional production. Because of the unique production method of 3D printing, the qualities of manufactured components are highly influenced by design and process variables.
Machine learning (ML) has been utilized in several ways in additive manufacturing to enhance the entire development and manufacturing process. Advanced data-based design methods for FFF and frameworks for optimizing FFF component design have already been developed.
Researchers estimated nozzle temperature with the help of machine learning suggestions. ML techniques were also used to calculate print bed temperatures and printing speed; equal sizes were set for all the specimens.
Results indicated that material flowability directly impacts the 3D printed output quality. Only the appropriate nozzle temperatures can ensure the materials' requisite flowability.
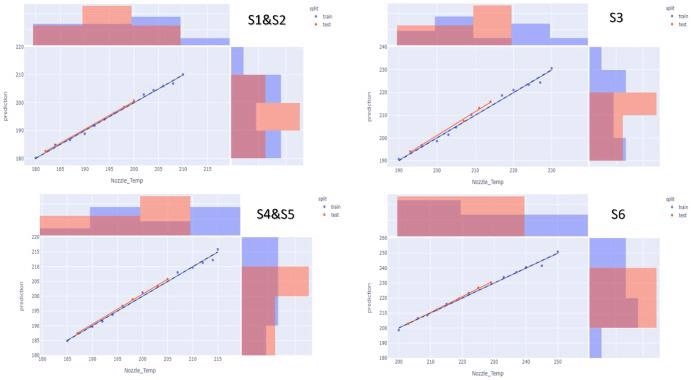
ML process optimization model validation for 3D printer. Image Credit: Hossain, M. I. et al
Fabrication of Nanoparticle Infused Plastic Products
In this work, PLA, HDPE, and recycled filament material mixed with TiO2 nanoparticles were used to create low-cost 3D printed items with a commercially accessible fused filament fabrication 3D printer and filament extruder.
The featured filaments were novel, and graphene was employed to generate a waterproof coating so that any changes to the fundamental mechanical characteristics of the finished products may be reduced. The exterior of the 3D printed component could also be treated.
The primary goal of this work was to discover a means to achieve more dependable and enriched mechanical and physical qualities in 3D printed items compared to commonly produced traditional 3D-printed items. The results and applications of this research could pave the way for developing numerous industry-related procedures.
Continue reading: What Nanoparticles are Best for Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing Applications?
Reference:
Hossain, M. I., Chowdhury, M. A., Zahid, M. S., Sakib-Uz-Zaman, C., Rahaman, M. L., & Kowser, M. A. (2022) Development and analysis of nanoparticle infused plastic products manufactured by machine learning guided 3D printer. Polymer Testing, 106. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014294182100372X?via%3Dihub
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.