Research published in the journal applied sciences has evaluated the antibacterial efficacy of antimicrobial viroblock/polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous webs generated by electrospinning to be used as viable protective clothing material.
Study: Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Containing Viroblock as Promising Material for Protective Clothing. Image Credit: Natale Zanardi/Shutterstock.com
Need of Protective Clothing
The SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) epidemic is an ongoing worldwide health disaster, impacting all aspects of life.
The scientific community has unparalleled difficulty finding viable medicinal remedies for the condition. COVID-19 infections are spread mainly through respiratory secretions. Viruses from particles larger than 20 µm have been known to remain anywhere from a few hours to many days on plastics, glassware, paper, and garment surface.
To slow the progression of the COVID-19 pandemic, health authorities advocate wearing face masks as a precautionary measure before vaccination is widely available.
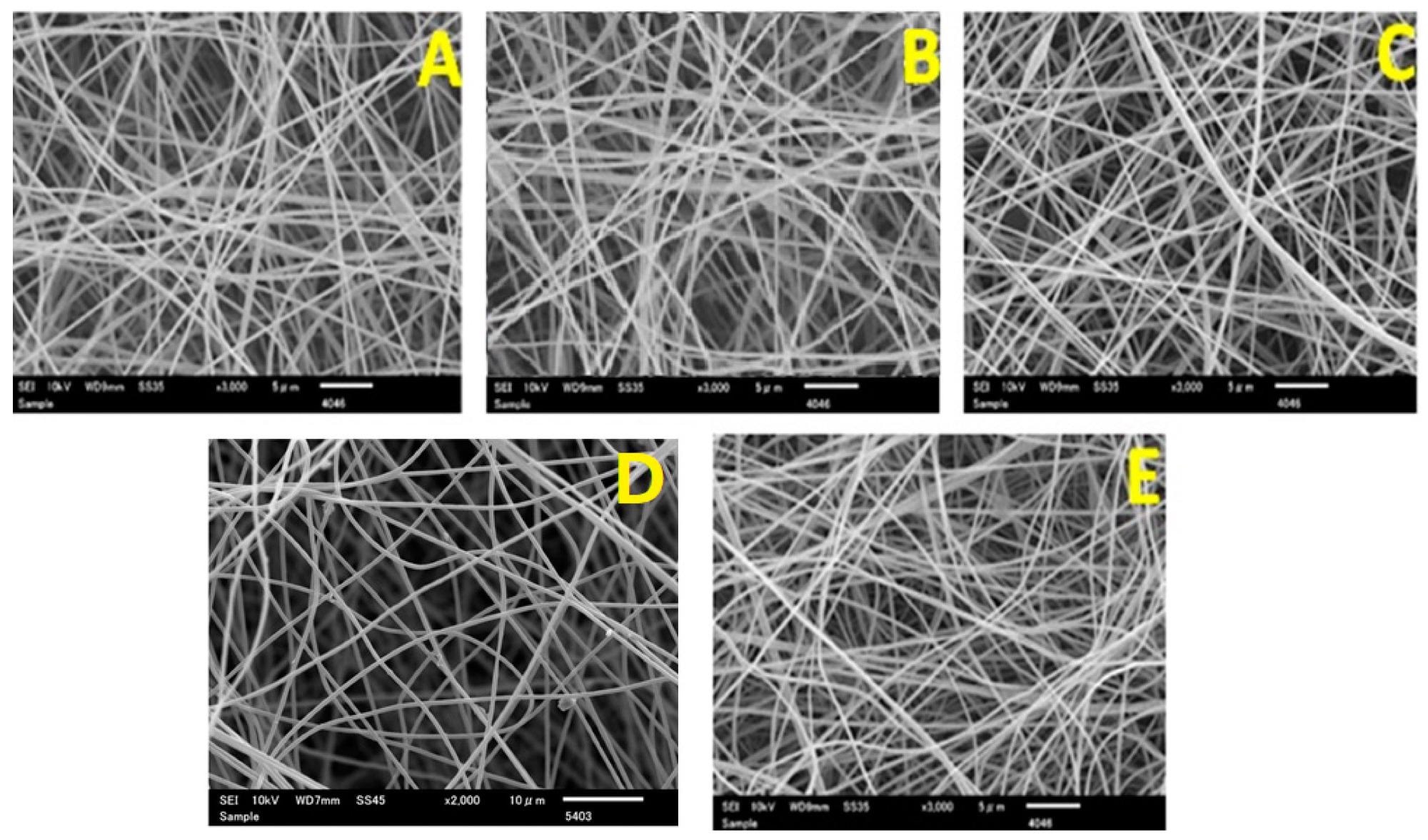
Surface morphology of prepared electrospun nanofibers: (A) pure PAN, (B) 0.5% VB PAN, (C) 1% VB PAN, (D) 1.5% VB PAN, and (E) 2% VB PAN. Image Credit: Hussain, M. et al.
Importance of Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials
Owing to their small hole diameters and high air penetration, nanofiber constituent membranes can be utilized as an efficient defensive shield against coronavirus infections.
Disposable micro and nanofibrous masks with particle filtration and antiviral characteristics have recently been made by immobilizing virus protection compounds. A viral deactivation technique that uses active chemicals and infuses them into nanofiber masks is effective.
Electrospun nanofibers are flexible and come in a variety of shapes and sizes with the ability to trap viruses due to their amorphous structure and porosity.
Air and water purifiers, biomedical engineering, medical equipment, geotechnical sciences, medication administrations, and power storage are just a few of the sectors where they are extensively utilized.
Nanoparticles made of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) have outstanding spinnability and mechanical behavior. PAN nanofibers have been widely employed in multiple industries, including purification and bulk synthesis of carbon fibers.
Nanoscale PAN screens with easily adjustable pore diameter, permeability, and wettability can be employed for protective covering technologies.
Importance of Viroblock
Viroblock is a mixture of aliphatic lipidic strands and certain cyclodextrins that can reduce the amount of lipid in antiviral walls. As a result of the silver infiltration, viral reproduction is inhibited, and infectious agents are killed.
Facemask testing revealed a 4-log reduction in treated vs untreated specimens, with long-term impacts on a variety of goods including drapes, medical garments, masks, and air filters.
The effectiveness of this bioactive chemical was demonstrated by a 4-log decrease in H1N1, H5N1, coronavirus, and other virus-associated respiratory diseases.
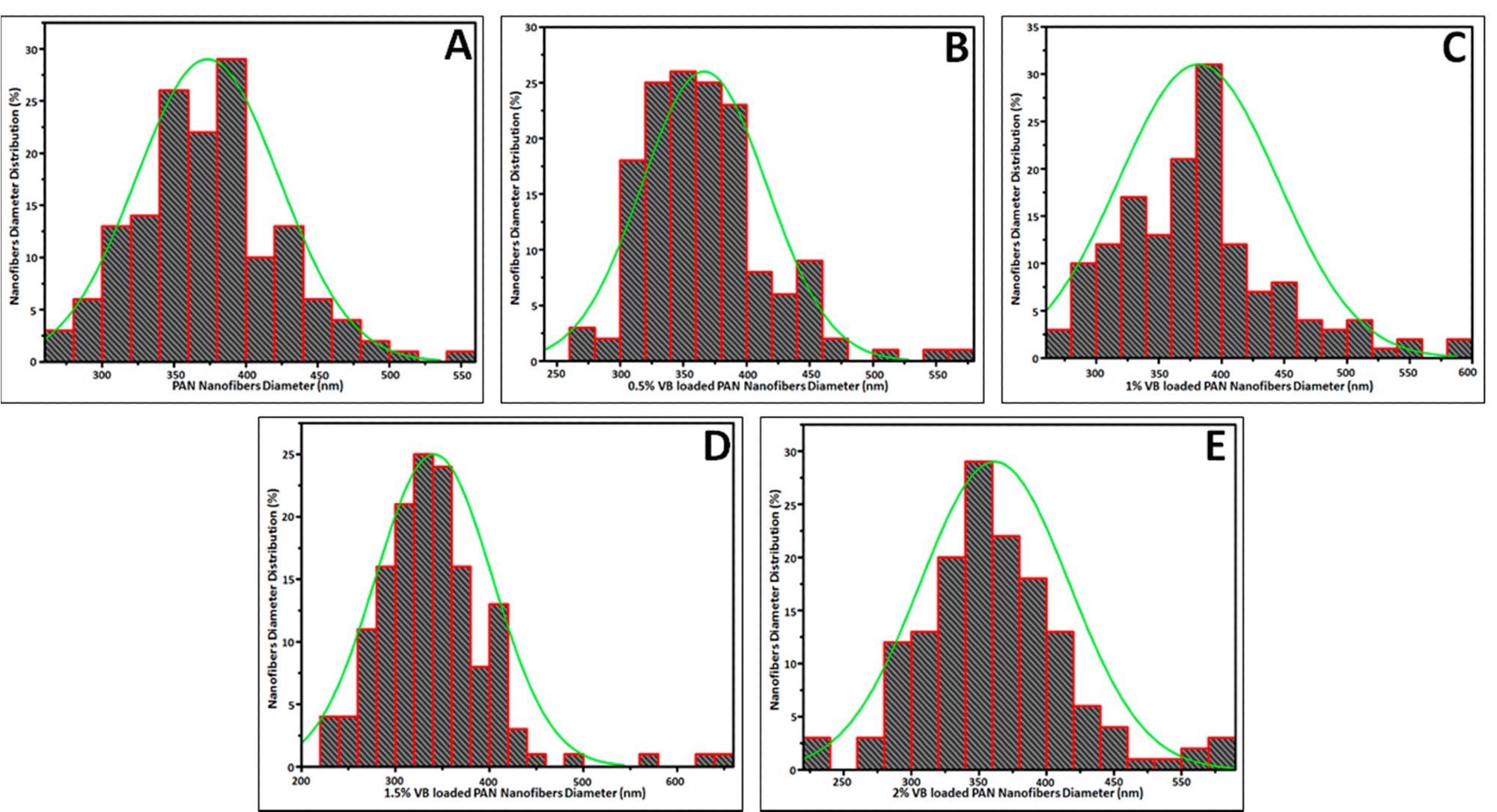
Diameter distribution curve: (A) pure PAN, (B) 0.5% VB/PAN, (C) 1% VB/PAN, (D) 1.5% VB/PAN, (E) 2% VB/PAN. Image Credit: Hussain, M. et al.
Research Findings
The surface structure of PAN electrospun nanofibers supplied with four varying concentrations of VB was investigated using SEM analysis. The size distribution of the nanofibers was determined to be 373.40 nm in the case of pure PAN electrospun nanofibers. The average size of the PAN electrospun nanofibers loaded with 0.5 percent VB was 366.55 nm, with a standard deviation of 49.55 nm.
Moisture content and water contact angle, which are essential characteristics determining a membrane's contamination susceptibility, confirmed the hydrophilicity. The results showed that the integration of VB in PAN nanofibers did not affect the water content values. All specimens had a water contact angle of fewer than 90 degrees, and all of the produced films were declared hydrophilic.
The results showed that when the proportion of VB in the VB/PAN nanofibers rose, the mass residue fractions of the VB/PAN nanofibers climbed. The quantity of Ag present in VB justified the pattern, as Ag was thermostable in this temperature range. An increase in VB concentration also resulted in decreased air permeability.
An MTT analysis was used to investigate the cytotoxicity of PAN nanostructures and VB/PAN nanofibers in biomedical applications. The cells were shown to be more robust with greater absorbency capacities of deposited formazan as the levels of VB increased. The vitality of all nanofibers improved with duration, indicating that the frameworks are suitable for metabolic activity and cell growth.
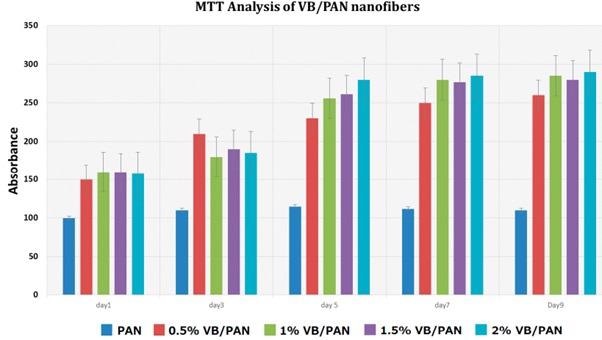
In Vitro Assessment Study: Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Containing Viroblock as Promising Material for Protective Clothing. Image Credit: Hussain, M. et al.
Silver infiltrated the bacteria after the walls were disrupted, engaging with sulfur-containing enzymes and causing decreased functioning and oxidative damage to DNA.
In short, the electrospinning process was used to effectively manufacture VB/PAN nanofibers with antiviral characteristics in this new study.
Higher loadings of VB considerably improved antimicrobial activities against E. coli and S. aureus, revealing the antibacterial actions of this chemical.
Continue reading: Antiviral Activity of Intermetallic Nanoparticles Incorporated into Polymeric Fibers.
Reference
Hussain, M. et al., (2021) Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Containing Viroblock as Promising Material for Protective Clothing. Applied Sciences, 11(23). 11469. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/11/23/11469/htm
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.