A recent study published in the journal Metals focuses on the development and applications of nano-copper particles as lubricant oil additives.

Study: Research Progress of Nano Copper Lubricant Additives on Engineering Tribology. Image Credit: Andrey VP/Shutterstock.com
Due to their exceptional qualities such as rapid sliding, high pressure, and self-repair, nano-copper particles can significantly increase the friction resistance and anti-wear efficiency of sliding parts. Additionally, their low yield stress and intergranular slip action results in a favorable synergistic action with other anti-friction and greasing compounds.
However, nano-copper particles are susceptible to aggregate during production, which severely limits their applications in a lubrication fluid system. Therefore, the modification of nanostructure and surface qualities has tremendous technical importance in increasing the production accuracy of nano-copper particles.
Characteristics of Nano-Copper Particles
Nano-copper's crystal has a face-centered cube arrangement (FCC), which results in nanoscale molecules and a quantum tunneling process. Additionally, the nanoscale particles have a low melting temperature (high thermal tolerance), a low shear toughness (easy to generate a sliding force on the surface), and a broad temperature range.
When subjected to friction, nano-copper particles demonstrate micro-ball rolling, self-healing, and coated film effects. They also exhibit superior durability, flexibility, and anti-wear qualities when used as a lubricating oil additive, advantageous for various engineering applications.
Nano-Copper Particles as Lubricating Oil Additives
With an increased emphasis on ecological preservation, the importance of sustainable lubricating oil additives is increasing to satisfy power-saving and emission-reduction requirements while adhering to high anti-friction and anti-wear industry standards.
Due to their extraordinary surface–interface impact and large specific contact region, nanoscale additives offer significant benefits in several industrial applications. While conventional lubricating oil additives may increase the lubrication effectiveness of tribo-pairs, their large reactive kinetic energy leads to corrosive wear, limiting their use in high-precision equipment's frictional components.
In comparison to conventional lubricating oil additives, nano-copper particles offer unmatched benefits such as a low energy restriction for film formation, no initiation time for the coating process, rapid formation of protective coating, and micro-bearing impact, further lowering fabrication and repair expenses and improving friction resistance and anti-corrosion effectiveness of sliding parts.
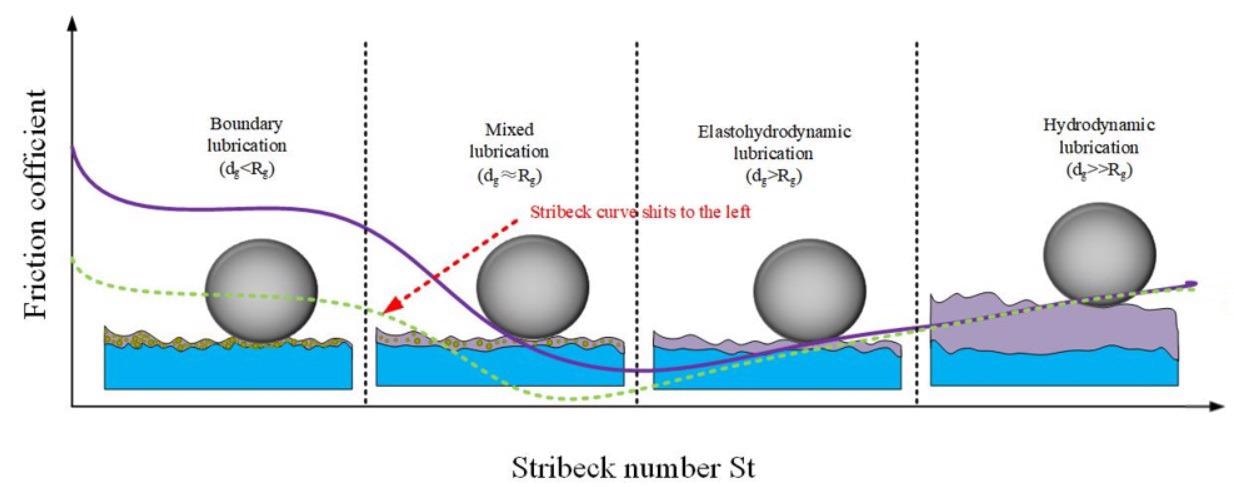
Effect of nano lubricant additive on Stribeck curve. © Guo, J. et al. (2021).
Limitations of Nano-Copper Lubrication Additives
Despite their many advantages, nano-copper particles lose their granular features due to high surface reactivity, primarily due to the presence of multiple unsaturated bonds on the nanoparticles' interface. Additionally, aggregation of nano-copper particles produced by Van der Waals' forces, electrostatic attraction, and H2 interaction between particles results in a rise in the size of secondary developing particles and the loss of nanoparticle properties.
This degrades the robustness of nano-lubricating oil devices and often results in oil clogs in commercial applications. As a result, it is critical to avoid the aggregation of nano-copper particles by maximizing suspension duration and dispersion stability.
Dispersion Stability of Nano-Copper Lubrication Additives
Surface treatment, polymer coating, and mechanical distribution can be used to increase dispersibility and prevent the aggregation of nano-copper particles. Physicochemical interactions between different surface modifiers change the interface of nanoparticles.
After surface treatment, features such as absorption, hydration, and diffusion of nanoparticles are modified to prevent particle build-up during the fabrication of nano-copper particles.
The polymer coating technique is a crosslinking method that employs additives to boost the oil absorption of nanoparticles during the production stage, hence increasing the lubricating oil's dispersibility.
Mechanical dispersion is a physical diffusion technique in which nanoparticles and solvents are combined by spinning, allowing nearby nanoparticles to be physically rubbed, completely absorbed, and distributed. This technology can be used to improve the size distribution of nano-copper particles and to expand the interfacial interaction between altered compounds and nano-copper particles.
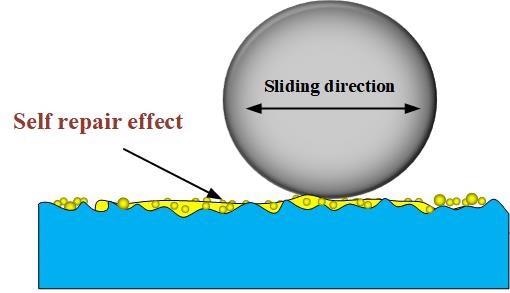
Schematic of lubrication enhancement of proposed lubrication mechanisms. © Guo, J. et al. (2021).
Conclusion and Prospects
This review discusses the advancement of research into the friction resistance and anti-corrosion capabilities of nano-copper particles as lubricating oil additives. Nano-copper particles are free of hazardous chemicals such as sulfur and phosphorus, which is helpful in several global initiatives taken for ecological perseveration and pollution reduction.
Nano-copper particles' efficacy and prospective uses in increasing the anti-friction and anti-corrosion qualities of lubrication oil are noteworthy. It is anticipated that copper nanoparticles can soon give rise to a new class of commercial lubricating oil additives.
Continue reading: How Can Nanoparticles Help in the Flow of Lubricants?
Reference
Guo, J. et al. (2021) Research Progress of Nano Copper Lubricant Additives on Engineering Tribology. Metals, 11(12), 2006. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4701/11/12/2006
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.