Polymer materials such as epoxy resins offer superior functional properties compared to other materials, and their properties can be altered to fulfill specific demands through structural alterations. An essential feature of polymer materials is their outstanding electrical shielding and cohesion. As a result, they are widely employed in motors, electrical packages, LED wrapping, aeronautical, and other industries.
Need of High Thermal Conductivity
As technology advances, electrical gadgets become compact while generating more heat. This increased heat emission is the source of heat buildup leading to a reduced service life of the electrical gadgets. Because of this, its thermal dissipation capability must be improved and its operating temperature must be kept within a healthy range.
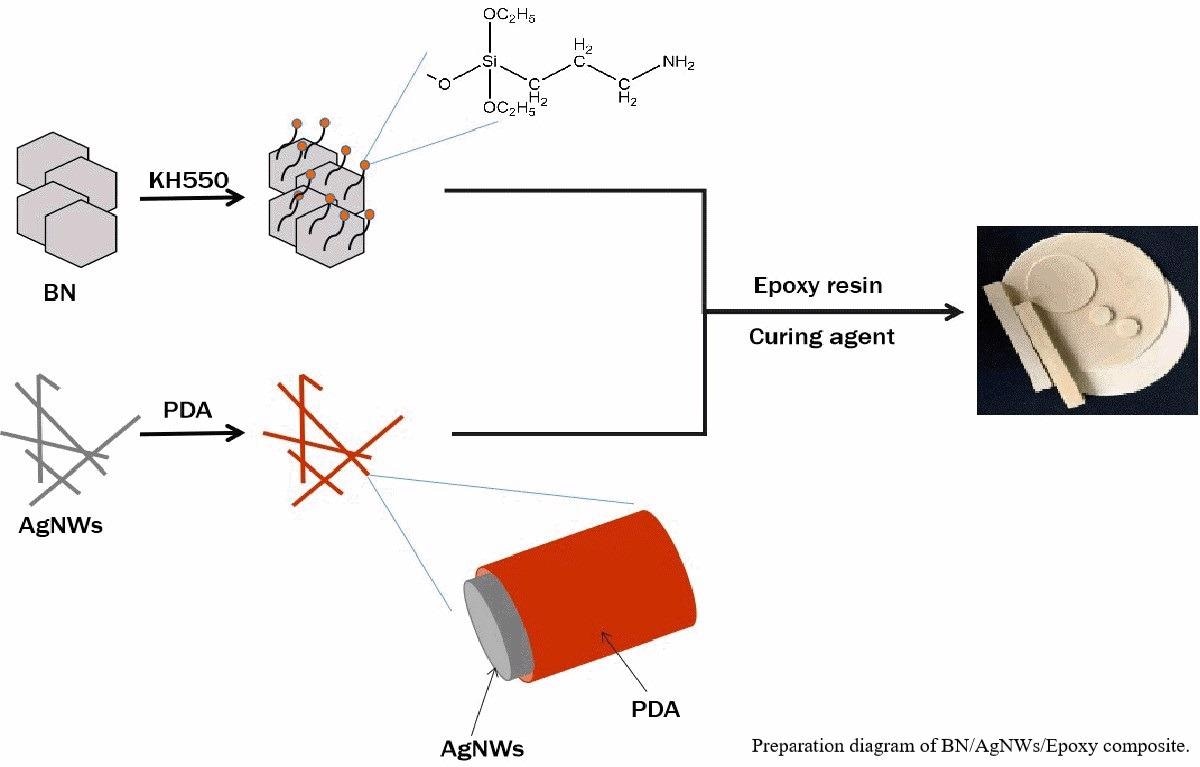
Preparation of BN/AgNWs/Epoxy composite. © Li, X., Weng, L., Wang, H. & Wang, X., (2021)
Limitations
Polymer materials' low heat conductance restricts their applicability. As a result, it is critical to create a polymeric epoxy matrix with good heat conduction and shielding.
Currently, the standard strategy is to choose specific inorganic nanoparticles with superior thermal properties as fillers, which are then mixed with polymeric materials to create superior temperature conductor composites. Metals such as aluminum, copper, and magnesium, as well as inorganic carbon compounds, are common fillers. Nevertheless, the high thermal conductivity of the these fillers greatly lowers the insulating of the nanocomposite, limiting their use in engines, electronic devices, and electrical gadgets.
Importance of Boron Nitride
Because of their dense molecular crystalline lattice, superior thermal conductance, and efficient electromagnetic shielding, nitride fillings have lately received increased attention.
Boron nitride (BN) is particularly adaptable, making it ideal for a wide range of purposes. BN and graphene can boost lateral heat transport within electrical and electronic systems, and the inclusion of BN can greatly increase the thermal conductivity of composites while not influencing their electrical insulating qualities.
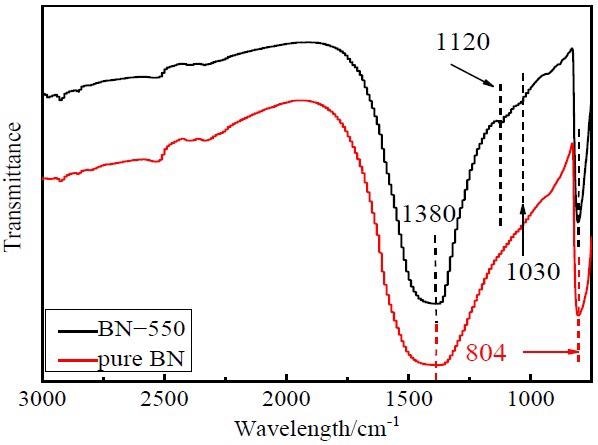
FT-IR spectra of pure BN and BN-550.© Li, X., Weng, L., Wang, H. & Wang, X., (2021)
Research Findings
It was revealed that resins with silver fillers had better storage modulus than others due to superior cross-linking of the layers of composites and filler. This is also a major factor in the enhancement of structural strength and integrity, leading to low deformation under stress.
The breaking toughness of the composites decreased as the quantity of AgNWs in the composite fillings was enhanced. The inclusion of BN reduced the mechanical performance of BN/EP to those of EP, but coupling agent and DA resulted in increased interlayer suitability and physical properties of composites. AgNWs and epoxy offered higher interface stability when coated with PDA. As a result, the declining trend in bending strength weakened. However, AgNWs were more prone to breaking when subjected to external stress because of their high aspect ratio.
The study also discovered that the higher the amount of AgNWs in composites fillings, the lesser the breakdown temperatures of the composite at the same phase. At the same time, composites with more AgNWs in their fillers had a reduced thermal breakdown temperature than those without.
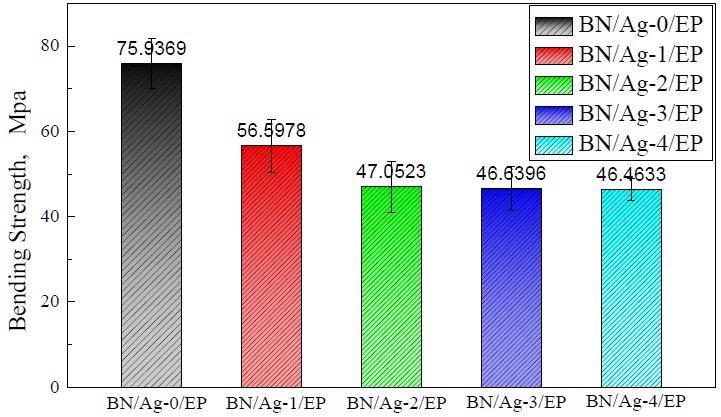
Bending strength of BN/AgNWs/EP composites.© Li, X., Weng, L., Wang, H. & Wang, X., (2021)
As AgNWs have a far superior thermal permeability than epoxy resins, a larger quantity of AgNWs was related to higher performance. It was discovered that the inclusion of BN increased the composite's heat capacity.
When AgNWs are not present, the BN nanofibers inside the matrices are not linked, allowing heat to flow extremely slowly between the BN nanostructure and readily dissipate. Furthermore, the inclusion of AgNWs finalized the matrix's thermal network of fillers.
The fact that the dielectric constant of the composite reduced as the AgNWs concentration increased was a key discovery. The dielectric constant of the composites dropped marginally when the mass ratio of AgNWs to BN fillers rose from 0/300 to 4/300.
To conclude, the addition of fillers enhanced the physical and thermal properties of the epoxy resins to ensure an enhanced lifespan.
Continue reading: Improving Epoxy Resin with Flower-Like Nanoparticles.
Reference
Li, X., Weng, L., Wang, H. & Wang, X., (2021) Nanoarchitectonics of BN/AgNWs/Epoxy Composites with High Thermal Conductivity and Electrical Insulation. Polymers, 13(24). 4417. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/13/24/4417
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.