A study published in the journal Sustainability investigated the introduction of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) to canola oil to improve its tribological properties.

Study: Synergistic Study of Solid Lubricant Nano-Additives Incorporated in canola oil for Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Sustainability. Image Credit: Chamille White/Shutterstock.com
Three nanoscale lubricating combinations were created by combining both GNP and hBN settings in varied ratios to get the best beneficial synergy.
Natural Oil Lubricants are Replacing Petroleum-Based Ones
In an effort to reduce the usage of lubricants based on petroleum, there is an increasing focus on the study of natural oils as lubricants for reducing abrasion and friction.
According to research, natural oils extracted from vegetables are less volatile, have greater lubricity, better load-carrying capabilities, larger index of viscosity, and better shearing stability in synthetic oils. Furthermore, these bio-oils exhibit improved dispersion behavior, reduced frictional losses, increased efficiency, a higher flash point, and greater power output.
Image of lubricant samples for (a) pure canola oil, (b) canola oil incorporated with hBN, and (c) canola oil incorporated with GNP. © Sikdar, S., Rahman, M. H., & Menezes, P. L. (2022).
Incorporation of Nanoparticles in Lubricants
Lubrication quality and performance may be increased by using low-weight percentages of nanoparticle (NP) and microparticle additions. One benefit is that it has a reduced coefficient of friction (COF) and wearing.
The ability of solid NPs to shear across contacting surfaces, along with their intrinsic multilayer architecture, is a crucial property for better lubricating qualities.
Pickering emulsions have previously been created with the addition of synthetic solid NPs like nanoscale clays. These mixtures might be employed as eco-friendly substitutes for a variety of uses, including food packing, restoration, and purification, to mention a few. NP size, shape, chemistry, and physical qualities determine the nature of NPs integrated into a lubricant.
Graphene Nanoplatelet Additives
Graphene is among the most noteworthy nanomaterials that is widely utilized as an additive in lubricating purposes. Graphene has high mechanical strength, excellent heat conduction, the capacity to reduce wear degradation, and is impermeable to fluids.
Because of such qualities, graphene has a distinct edge for use as an additive in lubrication. Furthermore, graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) are composed entirely of carbon and contain no toxic elements such as phosphorus or sulfur. As a result, they may be deemed eco-friendly.
Hexagonal Boron Nitride Additives
Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is a well-known solid lubricating agent with a lamella structure. It is renowned for having minimal friction in between the layers and the ability to form a protective barrier layer. Being white in hue, it is also colloquially known as white graphite.
In each layer of hBN, atoms of boron and nitrogen are bound to each other by powerful covalent bonding, while the layers are held together by weak Van der Waals forces. hBN powders are effective for reducing abrasive wear and frictional losses in a variety of settings. Furthermore, hBN is non-reactive to the vast majority of substances, making it ecologically safe. As a result, it is regarded as an intriguing ingredient for improving the effectiveness of lubricants.
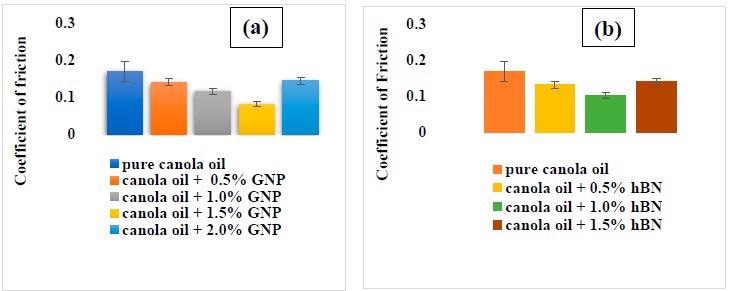
Coefficient of friction at the end of the test for pure canola oil and (a) canola oil with GNP, (b) canola oil with hBN. © Sikdar, S., Rahman, M. H., & Menezes, P. L. (2022).
Canola Oil – The Bio-Lubricant of Choice
Among the different bio-oils available today, canola oil is one of the least expensive and most widely accessible for use as a lubricant.
Canola oil exhibits surface tension and viscosity qualities comparable to some petroleum-based lubricating agents used in metal forming and stamping. In this study, the team investigated the effect of two distinct solid additives, GNP and hBN, integrated into canola oil individually and in conjunction.
Findings of the Study
The research revealed the remarkable enhancement in canola oil's tribological activity when combined with non-toxic additives such as hBN and GNP. The dynamic viscosity of canola oil was shown to rise with the integration of nanoscale additives.
When hBN and GNP are combined and mixed into canola oil, the abrasive wear and friction aspects improve significantly. When GNP and hBN are combined in canola oil to generate a hybridized nanoscale lubricant combination (particularly the blend having more hBN), a synergistic effect occurs in terms of the COF.
The hybrid combination with the highest GNP, on the other hand, had the least wear volume.
Continue reading: Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles in Biodegradable Lubricant Synthesis.
Reference
Sikdar, S., Rahman, M. H., & Menezes, P. L. (2022). Synergistic Study of Solid Lubricant Nano-Additives Incorporated in canola oil for Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Sustainability. Sustainability, 14(1). Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/1/290
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.