Due to its attractive properties in boosting light absorption, electron transport dynamics and surface reactions, graphene (GR) — a single-layer carbon sheet with a hexagonally packed crystalline lattice — has shown promising potential in artificial photocatalysis.
 This review overviews optimizing strategies and synthesis of graphene-based composite photocatalysts oriented by the fundamental manifold roles of graphene in photocatalysis and proposes the key challenges and future perspectives for further investigations of graphene-based photocatalysts. Image Credit: Chinese Journal of Catalysis.
This review overviews optimizing strategies and synthesis of graphene-based composite photocatalysts oriented by the fundamental manifold roles of graphene in photocatalysis and proposes the key challenges and future perspectives for further investigations of graphene-based photocatalysts. Image Credit: Chinese Journal of Catalysis.
Multifunctional GR-based photocatalysts, like GR-semiconductor, GR-metal and GR-organics, are now widely used in photocatalytic water splitting, environmental purification, carbon dioxide reduction and specific organic synthesis to provide a viable and long-term solution to the problems of energy scarcity and environmental crisis.
Due to the unique and fascinating properties of ideal GR, such as its 2D flat structure, relatively high specific surface area, excellent optical transmittance, efficient electron conductivity and chemical stability, GR has been shown to be a promising cocatalyst for improving the solar energy conversion efficiency of artificial photosynthesis systems.
Furthermore, in some photocatalytic systems, GR can operate as a macromolecular photosensitizer, generating photoelectrons on its own.
As is commonly recognized, the synthesis process used plays an important role in customizing the features of GR-based composites, including size, morphology, defect structure and surface/interface properties, all of which are connected to their photocatalytic efficacy.
To create high-efficiency GR-based composites with desirable architecture, a lot of time and effort has gone into researching and improving synthesis processes such as hydrothermal/solvothermal method, microwave-assisted synthesis, low-temperature oil bath method, combustion treatment, ultrasonication-assisted deposition, sol-gel approach, photo-assisted reduction and electrochemical deposition.
Prof. Yi-Jun Xu of Fuzhou University in China recently led a research group that examined the optimization methodologies and synthesizing of multifunctional GR-based composite photocatalysts.
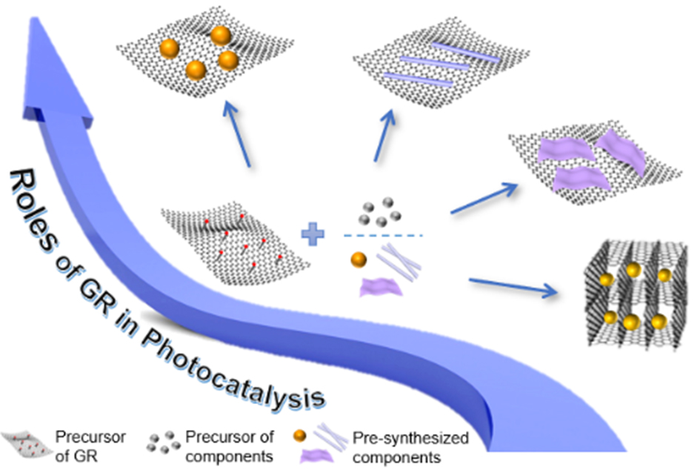
The optimization strategies for GR-based composites are first discussed, including reducing GR defect density, chemical doping, optimizing GR and photoactive component dimensionality, depositing cocatalysts to construct dual- or multi-cocatalyst systems, and enhancing interfacial parameters of GR-based composites.
The synthesis of GR-based composites is then examined from a novel viewpoint, centered on the roles of GR in photocatalysis, including photoelectron mediators and acceptors, enhancing adsorption capacity, customizing the light absorption range and intensity, and macromolecular photosensitizer.
A brief overview of the problems and possible evolution techniques for improving the solar energy conversion efficiency of GR-based composite is also presented. Chinese Journal of Catalysis published the study.
Journal Reference:
Li, Y-H., et al. (2022) Multifunctional graphene-based composite photocatalysts oriented by multifaced roles of graphene in photocatalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis. doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63871-8.