Levitated nanoparticles are considered useful tools with the ability to sense ultra-weak forces of chemical, biological, or mechanical origin and even for testing the basics of quantum physics.
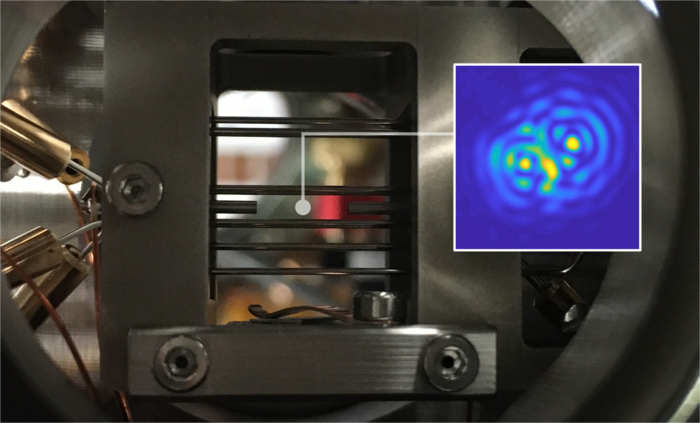 The ion trap used to levitate a single nanoparticle. Inset: optical interference between the particle and its mirror image. Image Credit: Quantum Interface Group, University of Innsbruck.
The ion trap used to levitate a single nanoparticle. Inset: optical interference between the particle and its mirror image. Image Credit: Quantum Interface Group, University of Innsbruck.
But such applications need accurate position measurement. Scientists at the Department of Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck, Austria, have currently illustrated a new method promoting the efficacy with which the position of a sub-micron levitated object has been detected.
Typically, we measure a nanoparticle’s position with a technique called optical interferometry, in which part of the light emitted by a nanoparticle is compared with the light from a reference laser. Laser beam, however, has a much different shape than the light pattern emitted by a nanoparticle, known as dipole radiation.
Lorenzo Dania, PhD Student, University of Innsbruck
At present, that shape difference restricts the measurement precision. Lorenzo Dania is a Ph.D. Student in Tracy Northup’s Research Group.
Self-Interference Method
This drawback is overcome in the new method presented by Tracy Northup, a professor at the University of Innsbruck, and her team by using the light of the particle reflected by a mirror in place of the laser beam.
The method is based on one that Rainer Blatt, also of the University of Innsbruck, and his group created recently to track barium ions. Scientists from the two teams suggested extending this method to nanoparticles last year. Now, the researchers demonstrated that this technique performed better than other cutting-edge detection techniques using a nanoparticle levitated in an electromagnetic trap.
The outcome opens up new avenues for using levitated particles as sensors, such as to measure minute forces, and for bringing the motion of the particles into the purview of quantum mechanics.
Financial support was offered, among others, by the European Union as well as by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, the Austrian Academy of Sciences, and the Austrian Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research.
Journal Reference:
Dania, L., et al. (2022) Position Measurement of a Levitated Nanoparticle via Interference with Its Mirror Image. Physical Review Letters. doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.013601.