A recent study published in the journal Scientific Reports focuses on the development of nanoscale lead sulfide (PbS) thin films using avocado leaf extracts via the chemical bath deposition technique.

Study: Synthesis of nano-sized lead sulfide thin films from Avocado (Glycosmis cochinchinensis) Leaf extracts to empower pollution remediation. Image Credit: Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock.com
Across the globe, a common trend is observed regarding the use of avocados (Glycosmis cochinchinensis): their fruit is consumed while leaves are left to pollute the environment.
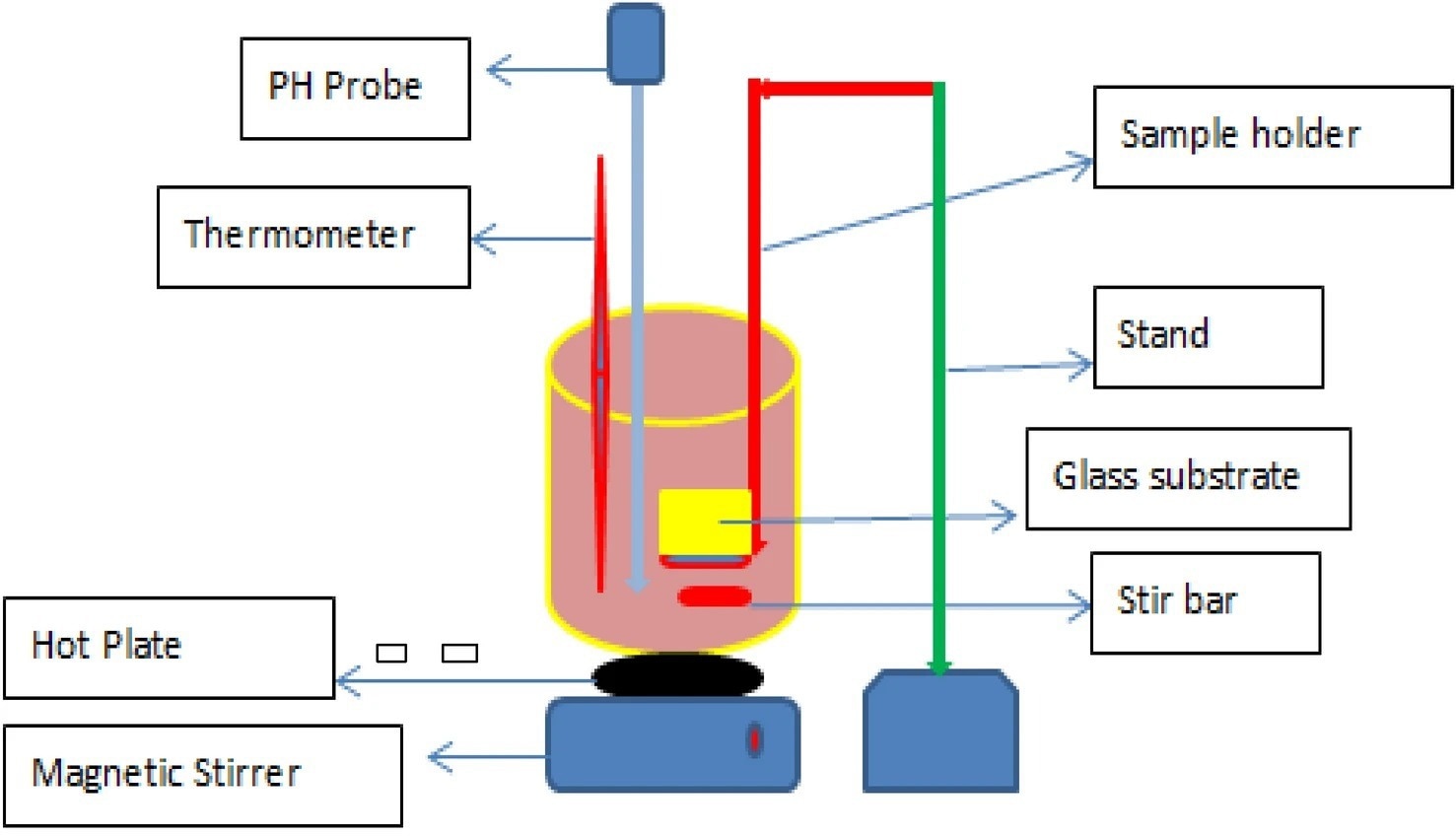
Figure 1. A schematic set of CBD method.
Nanomaterials have been extensively used in energy, optoelectronics, drug delivery, and ecological remediation applications because of their unique physicochemical, structural, optical, and gas detecting properties. However, the traditional methods for producing nanomaterials have raised several environmental concerns due to the use of harmful chemicals.
Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials: Why is it Important?
Green nanoparticle synthesis attempts to reduce waste and develop sustainable technologies. Green techniques that use moderate reaction conditions and nontoxic precursors have been highlighted in the development of nanotechnology in recent years to promote environmental sustainability.
Using bioactive agents such as plant materials, microbes, and other biowastes such as vegetable refuse, fruit peel waste, eggshell, and agricultural runoff are used in the green synthesis of nanomaterials. Using natural bioactive agents to manufacture metal nanoparticles minimizes the danger of environmental contamination significantly.
Lead Sulfide (PbS) Thin Films: Synthesis Methods and Advantages
Lead sulfide (PbS) is a semiconductor with a direct narrow energy gap at room temperature. Lead sulfide also has a positive temperature coefficient of the energy gap, rendering it with many unique physiochemical characteristics. Moreover, the photosensitive constants such as refractive index and extinction coefficients of lead sulfide thin films are optimum for optical sensing applications.

Figure 2. Avocado (Glycosmis cochinchinensis) Leaf extracts plant and its fruit taken from local area of Dambi Dollo Town, Oromia, Ethiopia.
Chalcogenide nanomaterials such as lead sulfide (PbS) thin films can play an essential role in many optoelectronic applications such as solar cells, gas sensors, laser materials, thermoelectric devices, and semiconductors.
PbS thin films have been prepared using various deposition methods such as spray pyrolysis, successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction, solid-vapor deposition, thermal evaporation, galvanic method, pulse electrodeposition, chemical bath deposition, and atomic layer deposition.
Benefits of Chemical Bath Deposition
Recently, the chemical bath deposition method has been used to produce PbS thin films.
The chemical bath deposition technique is a method of depositing thin films on a substrate from a solution containing metal, hydroxide, and sulfide or selenide ions. It has become an appealing technology because of its simplicity of manufacture, cheap cost, suitability for large-scale deposition regions, capacity to deposit thin films on various substrates, and ease of tweaking thin-film qualities by altering deposition settings.
The main benefit of this method is that it is feasible to guarantee that the reaction happening in the deposition bath occurs slowly throughout the formation of a film on a substrate, resulting in the production of thin films with outstanding interfacial characteristics.
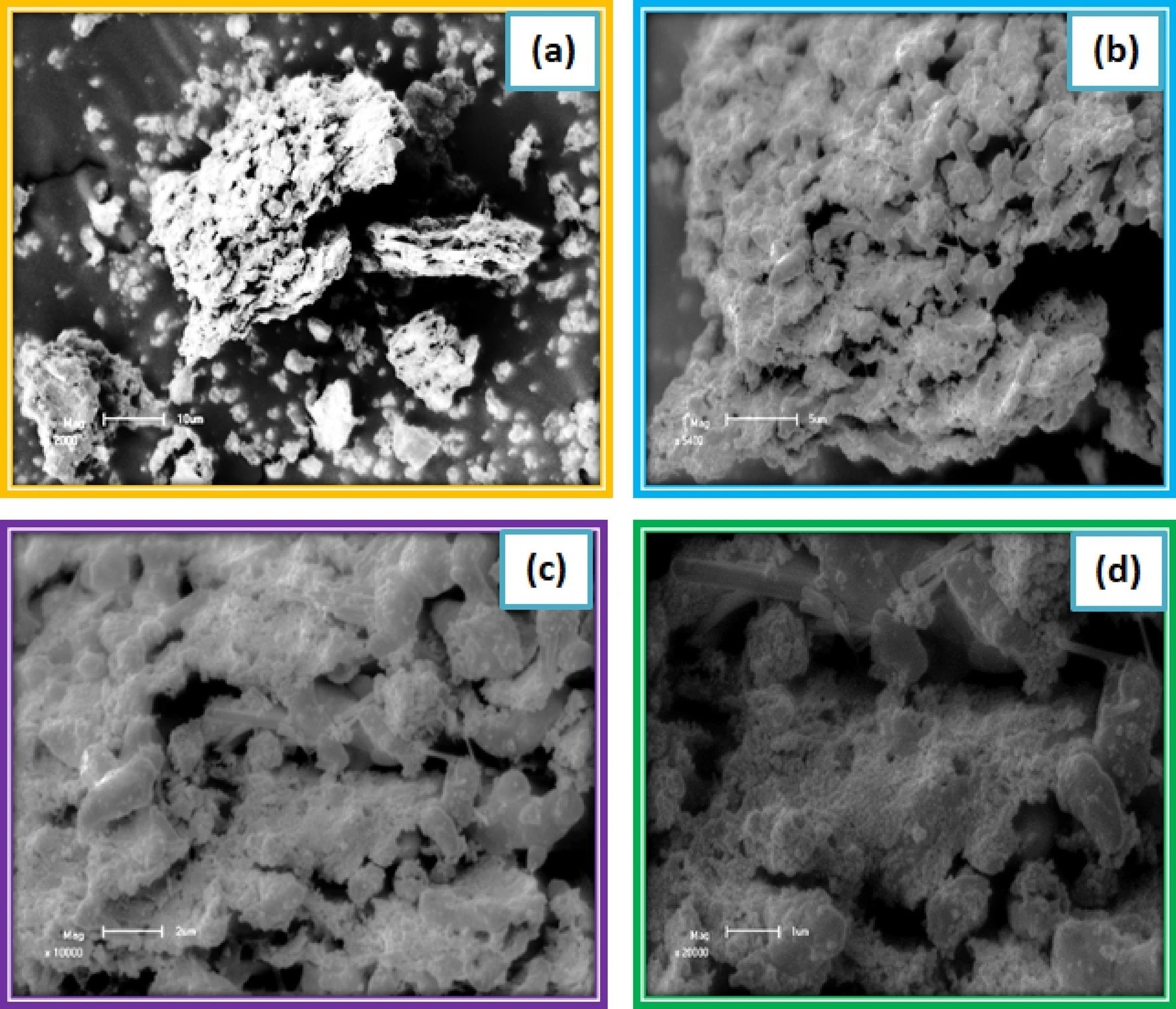
Figure 3. Scanning electron microscopic image of Lead Sulfide thin films from Avocado (Glycosmis cochinchinensis) Leaf extract at different PH values varied as (a) 2, (b) 4, (c) 6 and (d) 8.
Synthesis of PbS Thin Films Using Avocado Leaf Extracts
In the present study, nanocrystalline lead sulfide thin films were effectively produced using the chemical bath deposition approach from avocado plant leaf extracts. The thin films made were of exceptional quality. Various characterization techniques were used to explore the influence of concentration on the physical, structural, and optical aspects of PbS thin films.
The energy dispersive X-Ray analysis (EDX) method was employed to obtain the composition of the thin films. Then, the X-Ray photon spectroscopy (XPS) technique was utilized to obtain the chemical composition of the prepared films. The X-Ray diffraction (XRD) technique was also applied to study the structural properties of the prepared thin films.
XRD analysis revealed that the prepared nanomaterial is indeed a cubic crystal and the average crystalline size of the thin film is 0.5nm. The prepared thin films showed remarkable absorbance and little reflectance, making them suitable materials for use in solar cell applications.
The band gap of the nanocrystalline lead sulfide thin films prepared from avocado leaf extracts was found to be 2.43 eV which is higher than the bulk films because of quantum confinements of PbS nanocrystals. The samples prepared at pH=4, in particular, showed remarkable optical performance.
Based on these results, it is safe to suggest that lead sulfide thin films deposited from avocado leaf extracts are a promising resource for future applications in pollution management and sustainable energy generation.
Reference
Saka, A. et al. (2022). Synthesis of nano-sized lead sulfide thin films from Avocado (Glycosmis cochinchinensis) Leaf extracts to empower pollution remediation. Scientific Reports. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-15785-4
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.