As fossil fuel-based resources continue to deplete, alternative fuels are in high demand. A paper published in the journal Scientific Reports aimed to determine the efficiency of using waste fish oil biodiesel, mixed with nanoparticles, in a water-cooled single-cylinder IC engine.

Study: Use of waste fish oil biodiesel blended with aluminium oxide nanoparticle in IC engines: an experimental on performance, combustion and emission study. Image Credit: Africa Studio/Shutterstock.com
The Problem with Fossil Fuels
Growing industrialization has increased the need for fossil fuel-based products. When fossil fuels are consumed, a considerable amount of greenhouse gases are discharged into the environment, which is detrimental to the climate. Moreover, the growing need for fossil fuels is rapidly depleting the global crude oil reserves.
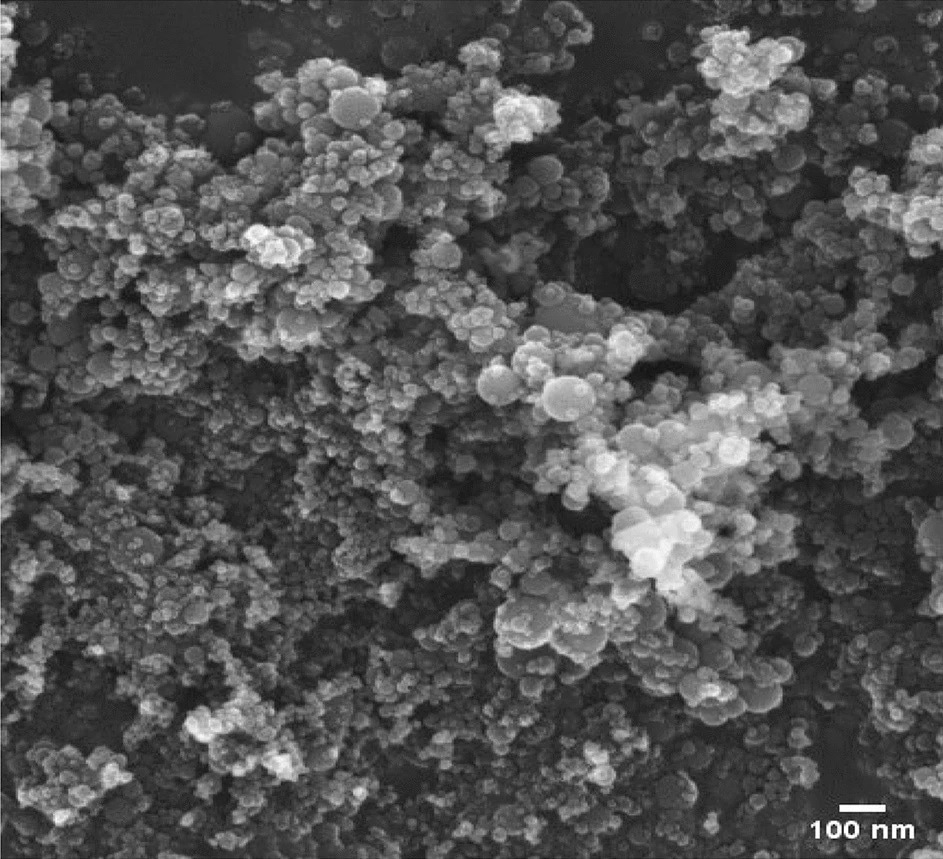

Figure 1. Aluminium oxide nano particles. Figure 3. Cumulative heat release with respect to crank angle. © Kannan, B. T., Sathish, T., Sathyamurthy, R., & Erko, K. G. (2022).
Fossil fuel supplies are limited and non-renewable; therefore, clean and alternate fuels are being encouraged globally.
Biodiesel – Fuel for the Future
Biodiesel has generated interest as a possible alternative fuel in IC engines because of its similar properties to diesel and capability to burn with lower exhaust emissions.
Biodiesel is a kind of alternate diesel fuel produced from sustainable biological resources like animal fats, vegetable oil, and fish oil. It is sustainable, non-toxic, biodegradable, and has reduced emission levels.
A large volume of fish waste is present in relevant disposal facilities. Utilizing this waste fish oil to produce useable biodiesel is highly beneficial for a sustainable future. Further enhancement of waste fish oil biodiesel is also essential.
Effects of Alcohol Content on Biodiesel
Using an increased alcohol concentration in biodiesel affects its heating value, viscosity, and cetane number.
Compared with butanol, propanol, and pure biodiesel, the combination of pentanol with biodiesel considerably lowered the brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC). The reduction in BSFC when incorporating pentanol as a biodiesel additive can be attributed to increased heating value and reduced enthalpy of vaporization.
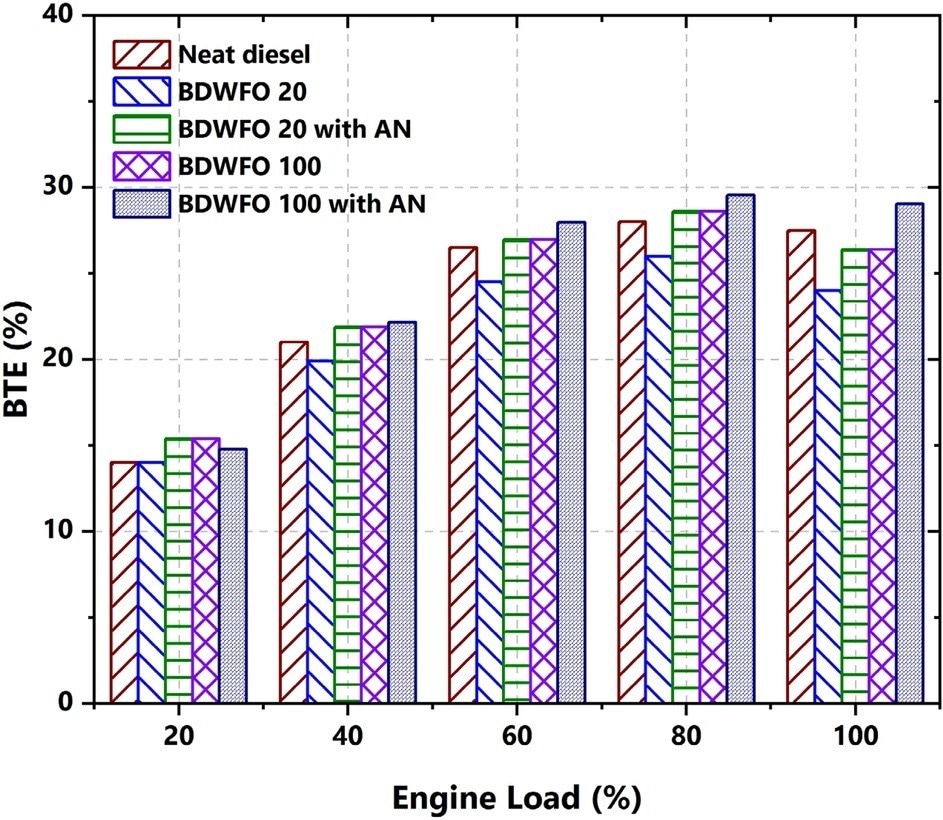
Figure 2. BTE—brake thermal efficiency (%) with respect to Load variation (%). Figure 3. Cumulative heat release with respect to crank angle. © Kannan, B. T., Sathish, T., Sathyamurthy, R., & Erko, K. G. (2022).
For an engine with 10% pentanol, the higher the thermal brake efficiency (BTE) and BSCF, the greater will be the exhaust gas temperature (EGT).
Nanoparticles as Fuel Additives
Incorporating nanoparticles in the waste fish oil biodiesel results in improved combustion and performance metrics. Oxygenation capabilities of the waste fish oil biodiesel blended with nanoparticles minimize exhaust emissions, including smoke, carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Aluminum oxide nanoparticles (Al2O3) endow diesel with superior emission characteristics, in contrast with copper oxide nanoparticles.
What Did the Researchers Do?
In this study, the team compared five experimental fuels: pure diesel, pure waste fish oil biodiesel (BDWFO 100), 20% waste fish oil biodiesel (BDWFO 20), Al2O3 nanoparticles incorporated in waste fish oil biodiesel, and Al2O3 nanoparticles incorporated in 20% waste fish oil biodiesel. The biodiesels were tested with identical operational conditions.
Among the different nanoadditives for biodiesel, Al2O3 nanoparticles have garnered the most interest because of their excellent physical and chemical characteristics, their good dispersion capability in biodiesel for increased performance, remarkable combustion properties and lower emissions.
Findings of the Study
The influence of waste fish oil biodiesel blended with Al2O3 nanoparticles on IC engine performance, emission levels, and combustion properties was investigated in this research.
The efficiencies of the examined fuels were comparable to that of diesel fuel. All the examined fuels, with or without nanoscale additives, had a slightly higher brake-specific energy consumption (BSEC) than diesel fuel.
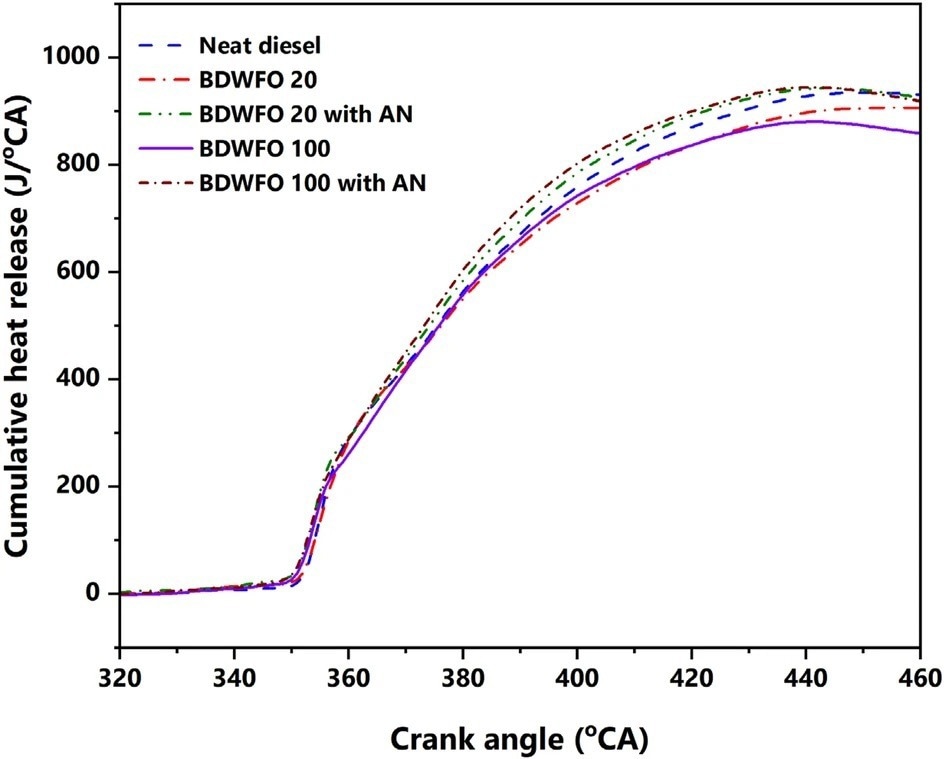
Figure 3. Cumulative heat release with respect to crank angle. © Kannan, B. T., Sathish, T., Sathyamurthy, R., & Erko, K. G. (2022).
According to combustion tests, the examined fuels had greater cylinder pressure and heat discharge rates than diesel fuel.
The carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions from the BDWFO 20 fuel with Al2O3 nanoparticles were fewer, while the carbon dioxide emissions were greater. The waste fish biodiesel with Al2O3 nanoparticles generated lower emissions, except for CO2.
Compared to conventional diesel fuel, the Al2O3 mixed waste fish oil biodiesel provided better performance and combustion with lower emissions.
Reference
Kannan, B. T., Sathish, T., Sathyamurthy, R., & Erko, K. G. (2022). Use of waste fish oil biodiesel blended with aluminium oxide nanoparticle in IC engines: an experimental on performance, combustion and emission study. Scientific Reports, 12. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-17059-5
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.