The α-reductase inhibitors, including β-sitosterol (BS) and phytosterol glycosides, are administered orally to cure androgenic alopecia and promote hair regrowth. However, they have poor bioavailability and solubility.
Study: Microneedle mediated transdermal delivery of β-sitosterol loaded nanostructured lipid nanoparticles for androgenic alopecia. Image Credit: Robert Przybysz/Shutterstock.com
An article published in the journal Drug Delivery presented a nanostructured lipid carrier (lipid nanoparticle)-based transdermal drug delivery system of BS and integrated it into polymeric microneedle (MN). The lipid nanoparticles were formulated via a rapid homogenization method, and the corresponding variables were optimized using the Box-Behnken statistical design.
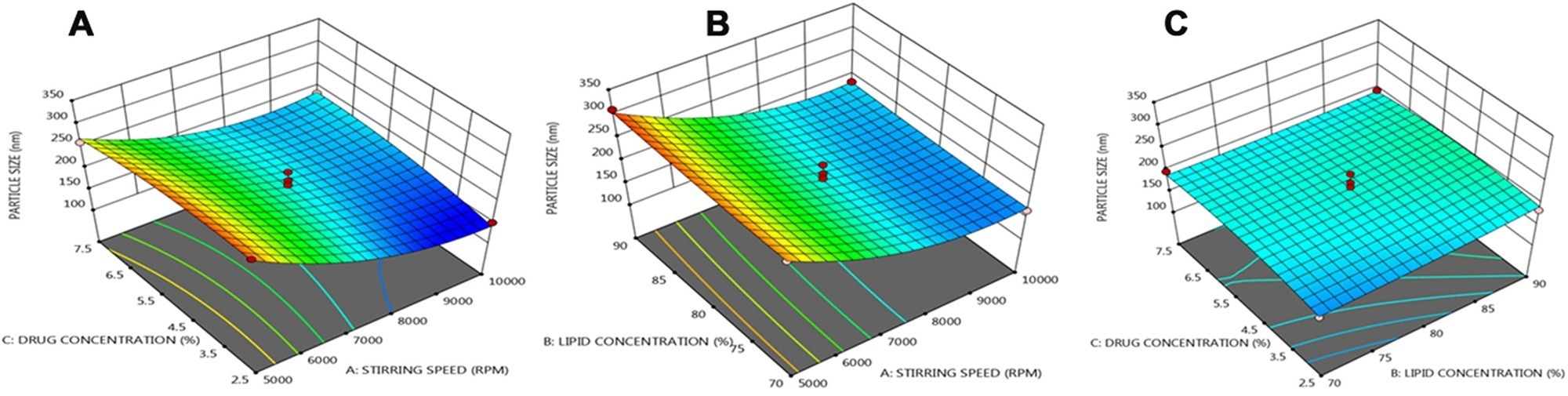
Three dimensional (3 D) response plots showing the effect of three variables on the particle size of NLCs. © Prabahar, K., Udhumansha, U., Elsherbiny, N., Qushawy, M. (2022)
Incorporating BS-loaded lipid nanoparticles into the chitosan-based MNs resulted in the fabrication of lipid nanoparticle-loaded polymeric MNs. The animal model evaluated the prepared MN-based lipid nanoparticles for androgenic alopecia. The results revealed that the amount of BS associated with MN-based lipid nanoparticles that penetrated the skin of a rat in vitro was 3612.27 ± 120.81 micrograms per square centimeters, while that from lipid nanoparticles alone was 2402.35 ± 162.5 micrograms per square centimeters.
Compared to the optimized pure lipid nanoparticles formulation, the steady-state flux (denoted as Jss) of MN-based lipid nanoparticles was substantially higher. Moreover, the ratio of Anagen/telogen was affected by MN-based lipid nanoparticles and pure lipid nanoparticles, which were 1.24 ± 0.18, and 2.22 ± 0.34, respectively.
Treating hair loss induced by androgen in rats treated with BS indicated hair follicle dominance during the anagenic development. Nevertheless, the MN-based lipid nanoparticle delivery method has significantly improved rats’ hair growth. These experimental results led to the conclusion that the MN-based transdermal system with lipid nanoparticles had the potential to be a successful therapy for androgenic alopecia.
Treatment for Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male-pattern baldness, is the classic thinning of the hair that occurs in middle-aged men. The testosterone hormone plays a crucial role in male androgenetic alopecia, regardless of genetic predisposition.
In the cells of the hair follicle, testosterone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5α-reductase that exists as two isoenzymes: type I and type II, and the latter, expressed in the hair follicles and other androgen-dependent tissues, appears to be particularly important in male pattern baldness.
Androgen activity is mediated by binding to the human androgen receptor, and the receptor-ligand complex regulates the expression of androgen-sensitive genes, acting as a transcription factor. Initially, androgenetic alopecia was treated with FDA-approved finasteride, a 5-hydroxysteroid reductase inhibitor. Since it can cause sexual dysfunctions, myalgia, and testicular pain, a safe alternative to finasteride with an effective therapeutic strategy is in great demand.
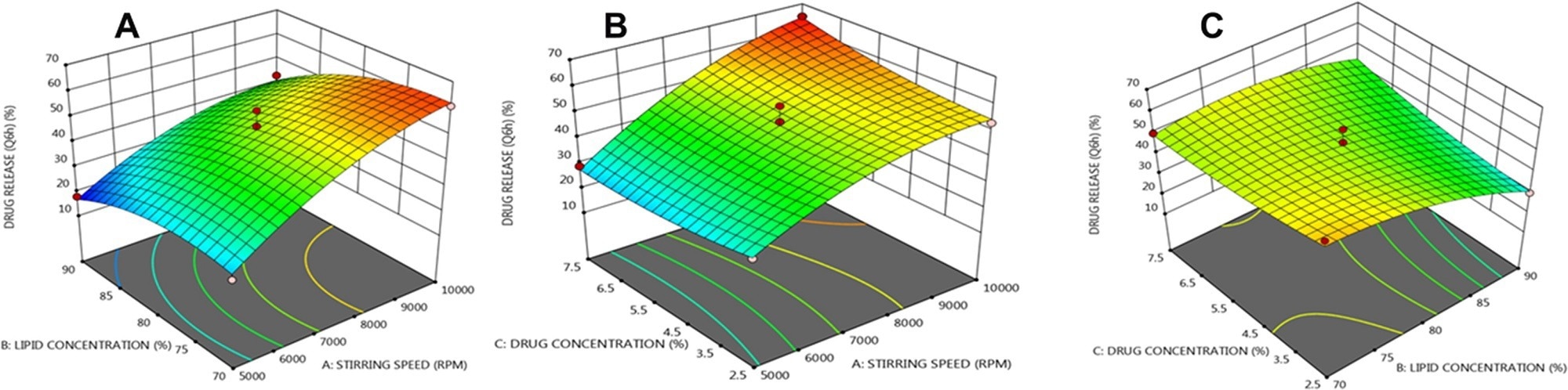
Three dimensional (3 D) response plots showing the impact of three variables on the β-sitosterol release from NLCs. © Prabahar, K., Udhumansha, U., Elsherbiny, N., Qushawy, M. (2022)
BS is a naturally occurring phytosterol found in fruits, leaves, and rhizomes. Diverse pharmacological properties of BS, including angiogenic, antidiabetic, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory, have been identified in previous studies. BS's ability to inhibit 5'-reductase has led to its usage in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. The primary challenges in the oral administration of BS are its limited oil and water solubility, high daily doses, and crystalline form at body and room temperatures.
In this regard, to increase the therapeutic effectiveness by enhancing BS oral absorption, complexation with liposomal, cyclodextrin, solid lipid nanoparticles, electrospun nanofibers, and self-emulsion drug delivery systems (SMDDS) have all been explored. The effective incorporation of BS in pharmaceutical formulations is a challenging phenomenon.
BS-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for Treating Androgenic Alopecia
The nanosized therapeutics have high skin contact and regulated drug release, which has inspired the designing and fabrication of BS-loaded lipid nanoparticles for topical application. Lipid nanoparticles are primarily employed as carriers for lipophilic compounds because their strong affinity for the lipid phase leads to a high loading capacity.
In the present study, lipid nanoparticles based MNs were formulated successfully to increase the transdermal penetration of BS compared to the BS formulation with only lipid nanoparticles. The chitosan-based MNs served as reservoirs that regulated the controlled release of BS. The capacity of MNs to circumvent the barrier characteristics of the stratum corneum has improved transdermal medication delivery.
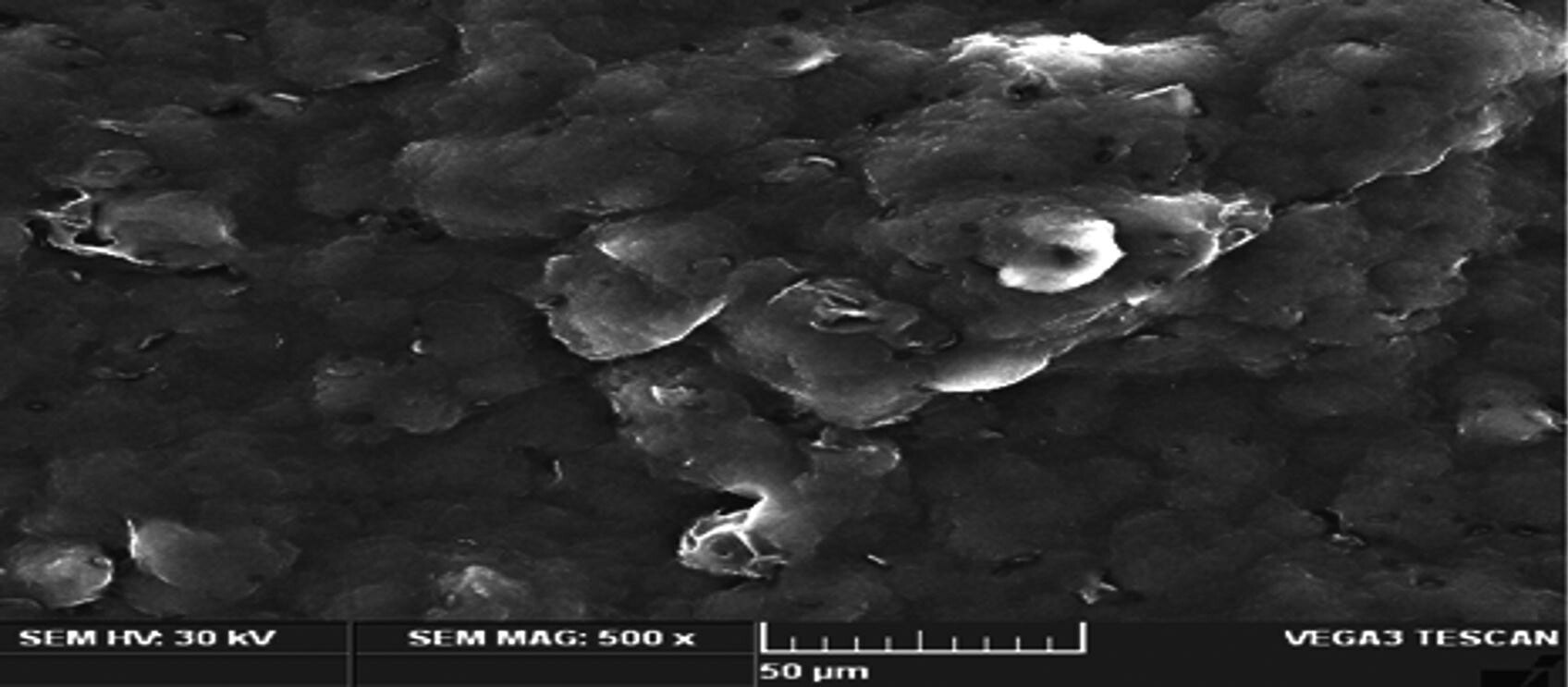
SEM images of the optimized β-sitosterol loaded NLC formulations. © Prabahar, K., Udhumansha, U., Elsherbiny, N., Qushawy, M. (2022)
The findings revealed that while the formulation with lipid nanoparticles alone released 2402.35± 162.5 micrograms per square centimeters of BS, the amount released with lipid nanoparticle-MN penetration was 3612.27±120.81 micrograms per square centimeters.
The Jss of the lipid nanoparticle-MN was significantly greater than pure lipid nanoparticles. This finding showed that the in vitro percutaneous penetration rate of the BS-loaded lipid nanoparticles integrated into MNs was higher than that of the plain lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery system.
Conclusion
To conclude, this work has focused on how the transdermal administration of BS increases the local concentration of active molecules. Based on the technology and data presented in the current work, MN-based nanomedicines have a high scope of scaling up through an easy process.
Androgenic alopecia and other illnesses linked to androgens could be treated by topical application of BS-loaded lipid nanoparticles based on MNs, which has high scope for commercialization.
Reference
Prabahar, K., Udhumansha, U., Elsherbiny, N., Qushawy, M. (2022). Microneedle mediated transdermal delivery of β-sitosterol loaded nanostructured lipid nanoparticles for androgenic alopecia. Drug Delivery. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10717544.2022.2120927
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.