Deyu Li and Josh Caldwell, both Professors of Mechanical Engineering at Vanderbilt, are part of a team of researchers who discovered a new heat dissipation channel using phonon polaritons that could have far-reaching implications for novel cooling technologies in devices such as smartphones and other modern electronics.
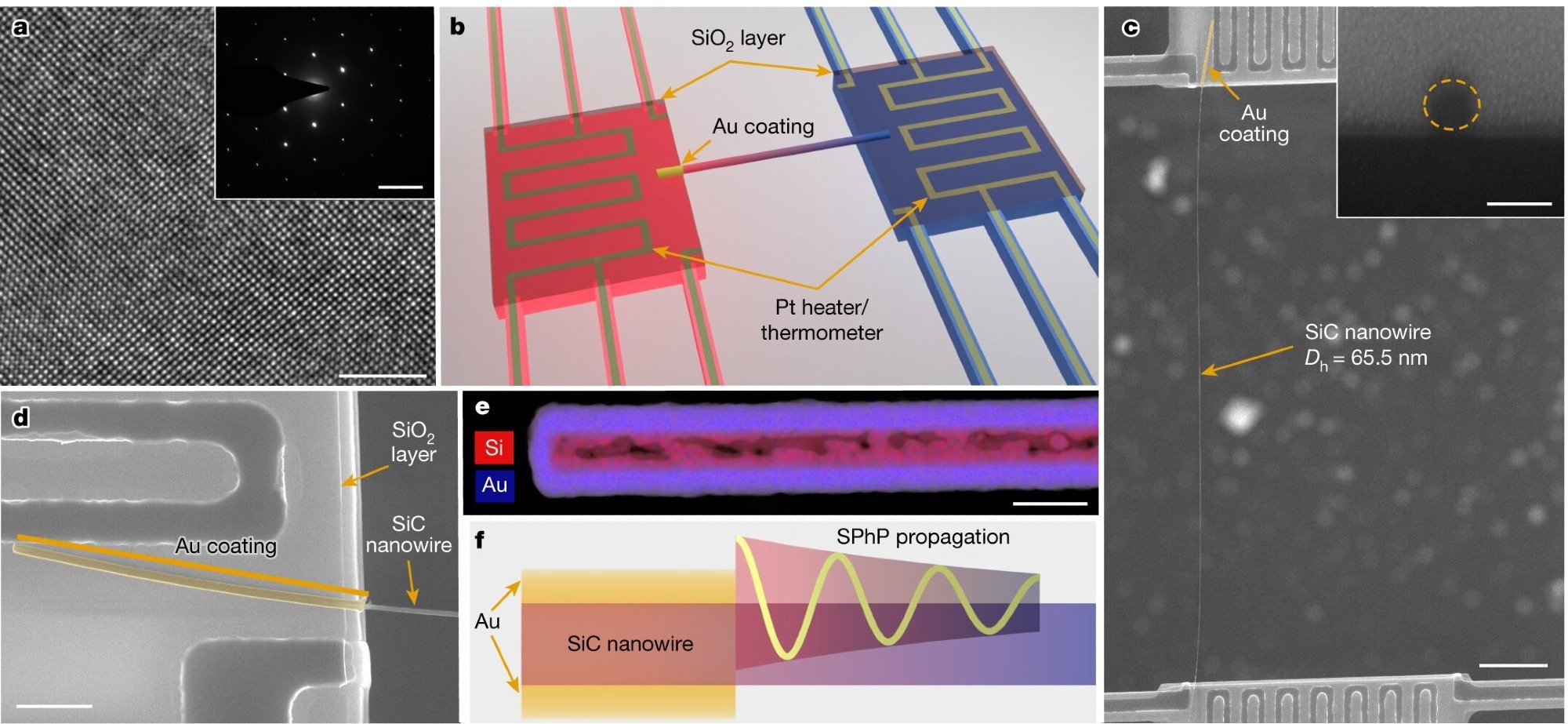 SiC nanowire sample and measurement scheme. a, A high-resolution transmission electron microscopy micrograph of a 65.5-nm diameter SiC nanowire (Sample S1). Inset, selected area electron diffraction pattern indicating the 3C-SiC structure. Scale bars, 5 nm, 5 nm−1 (inset). b, Schematic illustration of a SiC nanowire with Au coating on one side placed on the measurement device. c, An SEM micrograph of Sample S1 placed on the measurement device. Inset, cross-section of the wire. Scale bars, 5 μm, 100 nm (inset). d, A zoom-in SEM micrograph of the Au-coated end on the suspended membrane. For all measurements, the Au-coated portion protruded from the membrane for <200 nm. Scale bar, 1 μm. e, Element mapping of the Au-coated portion of a nanowire sample (Sample S8). Scale bar, 100 nm. f, Schematic illustration of SPhP propagation along nanowires. Image Credit: Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06598-0
SiC nanowire sample and measurement scheme. a, A high-resolution transmission electron microscopy micrograph of a 65.5-nm diameter SiC nanowire (Sample S1). Inset, selected area electron diffraction pattern indicating the 3C-SiC structure. Scale bars, 5 nm, 5 nm−1 (inset). b, Schematic illustration of a SiC nanowire with Au coating on one side placed on the measurement device. c, An SEM micrograph of Sample S1 placed on the measurement device. Inset, cross-section of the wire. Scale bars, 5 μm, 100 nm (inset). d, A zoom-in SEM micrograph of the Au-coated end on the suspended membrane. For all measurements, the Au-coated portion protruded from the membrane for <200 nm. Scale bar, 1 μm. e, Element mapping of the Au-coated portion of a nanowire sample (Sample S8). Scale bar, 100 nm. f, Schematic illustration of SPhP propagation along nanowires. Image Credit: Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06598-0
The study, titled “Remarkable Heat Conduction Mediated by Non-equilibrium Phonon Polaritons", was published in the journal Nature.
It is commonly recognized that the main energy carriers in solids are electrons and phonons, which are vibrations of atoms. Researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and Vanderbilt University were taken aback when they discovered that heat conduction in polar crystal thin films and nanowires could be significantly helped by surface phonon polaritons, hybrid quasi-particles produced by coupling infrared light and optically active phonons.
Although it has been hypothesized that surface phonon polaritons aid in heat conduction in polar thin films and nanowires, there has not yet been concrete experimental proof. The Vanderbilt study team was able to show that SiC nanowires with and without metallic polariton launchers at the ends had noticeable increases in heat conductivity.
The substantial heat transfer capabilities of these polaritons can be engineered into novel cooling strategies, which are critical for a wide variety of technologies from consumer electronics to efficient building environment control. This discovery may contribute to better living and efforts geared towards combating climate change.
Deyu Li, Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Vanderbilt University
Many applications of infrared nanophotonics research are centered around phonon polaritons, according to Caldwell.
I was excited to see that they can also provide a new heat dissipation channel, opening additional areas of impact, for instance, ultrafast cooling in high-frequency and high-power electronic devices.
Josh Caldwell, Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Vanderbilt University
Journal Reference:
Pan, Z., et al. (2023) Remarkable heat conduction mediated by non-equilibrium phonon polaritons. Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06598-0