In a new study, scientist Rajiv K. Saxena and his team investigated the potential of nanodiamonds in combating tumor metastasis.
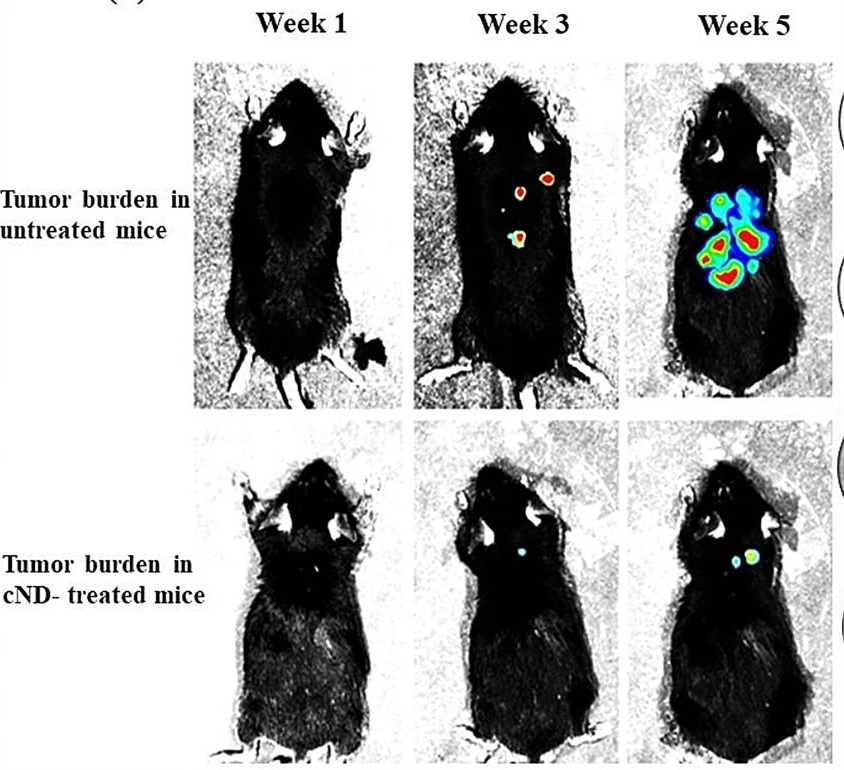 Effect of treatment with carbon nanodiamonds on the growth and metastasis of B16F10-Luc2 tumor in mice by bioluminescence imaging. Image Credit: Behera et al
Effect of treatment with carbon nanodiamonds on the growth and metastasis of B16F10-Luc2 tumor in mice by bioluminescence imaging. Image Credit: Behera et al
Nanodiamonds, carbon nanoparticles ranging from 2-8 nm in size, are known for their easy functionalization with various groups, including carboxylic groups or drugs. Earlier research has established that actively dividing cells have a higher propensity to absorb nanodiamonds. Notably, epithelial cells treated with carboxylic nanodiamonds exhibited an impaired ability to traverse cell-permeable cellulose membranes.
Focusing on melanoma, a cancer known for its high metastatic potential, the researchers treated B16F10 melanoma cells with carboxylic nanodiamonds in a controlled environment. They then assessed the cells' migratory and invasive capabilities across polycarbonate membranes featuring 8 µm pores. The findings were revealing: melanoma cells exposed to nanodiamonds were hindered in their ability to migrate, unlike their untreated counterparts, which easily passed through the membrane.
The study extended to in vivo models, where C57Bl/6 mice inoculated with B16F10 melanoma cells were treated with carboxylic nanodiamonds. Remarkably, these mice exhibited minimal or no metastasis, in stark contrast to untreated mice, where tumors not only grew but also spread to new body areas. Furthermore, the survival rate of the nanodiamond-treated, tumor-bearing mice was significantly higher compared to their untreated counterparts.
Gene expression analysis led the authors to theorize that nanodiamonds may block cancer cell detachment from primary tumors and inhibit subsequent metastasis stages, including cell movement and entry into blood vessels. Given these promising results, Saxena and colleagues advocate for further exploration of nanodiamonds as a therapeutic agent in the battle against cancer metastasis.
Journal Reference:
Behera, S. P., et. al. (2023) Carboxyl nanodiamonds inhibit melanoma tumor metastases by blocking cellular motility and invasiveness. PNAS Nexus. doi:10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad359