Researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology demonstrated a breakthrough in holographic polymer nanocomposites using the liquid crystal E6M. This method marks a major breakthrough in augmented reality technology by improving refractive index modulation while lowering haze and opening the door for more effective and portable AR systems. The Chinese Journal of Polymer Science published this study.
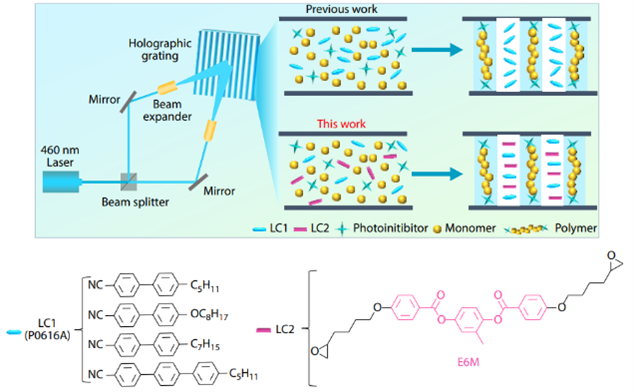 Schematic illustration on the construction of high-performance LC-based holographic polymer nanocomposites by doping E6M. P0616A was commercially available LC in nematic phase. Image Credit: Chinese Journal of Polymer Science.
Schematic illustration on the construction of high-performance LC-based holographic polymer nanocomposites by doping E6M. P0616A was commercially available LC in nematic phase. Image Credit: Chinese Journal of Polymer Science.
In augmented reality displays, holographic optical elements (HOEs) are crucial because they offer advantages such as enhanced optical efficiency and design flexibility. Unfortunately, performance is hampered by the restricted refractive index modification of existing materials, especially when trying to achieve a wider field of view and higher brightness.
To overcome these obstacles, scientists are currently concentrating on creating materials that can improve refractive index modulation, which is the basis of this research.
An important development is the study's incorporation of E6M into polymer nanocomposites. By attaining a refractive index modulation of 0.050 at 633 nm and preserving haze at a mere 5.0% with a 5-weight percent concentration, the liquid crystal improves molecular alignment.
The difficulty of balancing optical performance with material thinness is addressed by these advancements, which result in a high diffraction efficiency of 96.2% with a minimum thickness of 5 μm. For next-generation augmented reality devices, efficiency and compactness are critical, which makes the composites perfect.
Our work demonstrates a major improvement in the optical performance of holographic polymer nanocomposites, which could transform AR device design. Achieving high diffraction efficiency with minimal thickness sets the stage for thinner, lighter, and more efficient AR displays.
Hai-Yan Peng, Study Corresponding Author and Professor, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
The AR sector stands to benefit greatly from sophisticated holographic polymer nanocomposites, particularly in the development of future display technologies. By achieving great optical performance with decreased material thickness and low haze, more compact and effective augmented reality systems can be constructed.
This development may lead to a greater uptake of AR technology in industries such as healthcare, education, and entertainment, improving user experiences and promoting innovation in the field.
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Innovation and Talent Recruitment Base of New Energy Chemistry and Device. Analytical assistance from HUST Analytical & Testing Center, and Core Facilities of Life Sciences is also acknowledged.
Journal Reference:
Wang, M.-Y., et al. (2024) Holographic Polymer Nanocomposites with High Refractive Index Modulation by Doping Liquid Crystal E6M. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science. doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3110-z.