Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Oct 9 2024
Scientists from the City University of Hong Kong found a significant energy loss in metal nanostructures. By varying their geometrical dimensions, they have fully tapped into these structures' potential, opening the door to the creation of more potent and effective nanoscale optical devices. The research was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
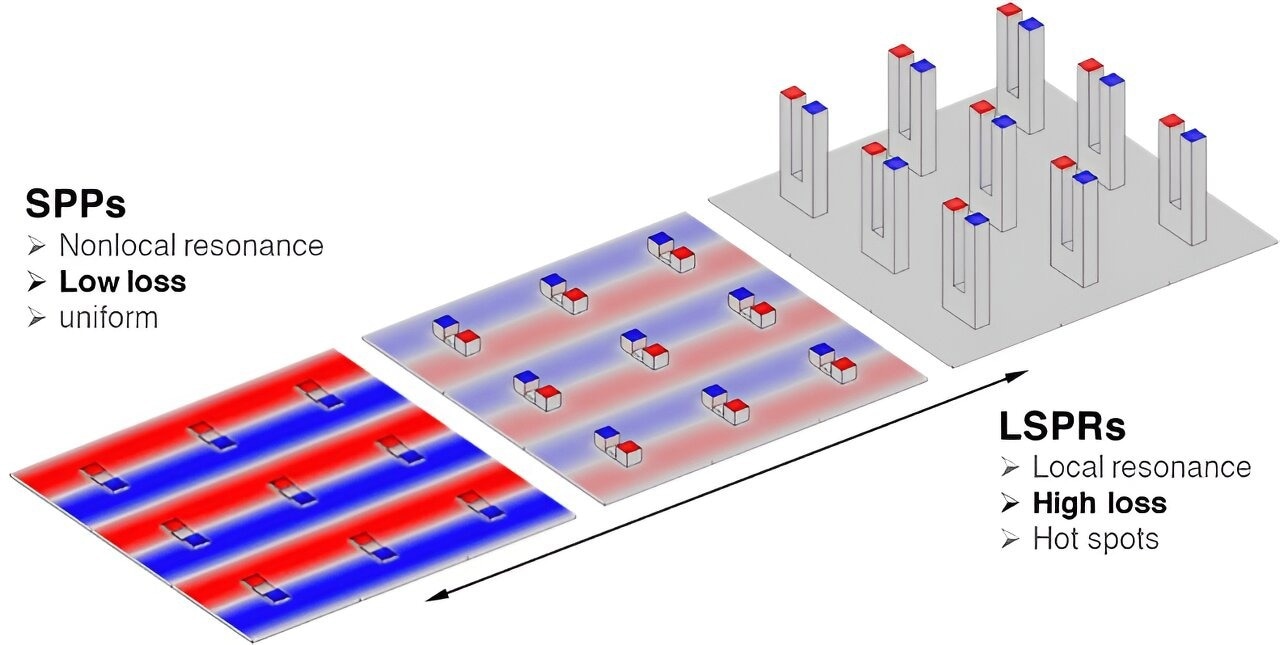 Height reduction in metal arrays shifts resonance from LSPRs to SPPs. Image Credit: Physical Review Letters
Height reduction in metal arrays shifts resonance from LSPRs to SPPs. Image Credit: Physical Review Letters
Professor Tsai Din-ping, Chair Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering at CityUHK, and Professor Yuri Kivshar from Australian National University share leadership of the research team. In 2023, Professor Kivshar also held the position of visiting research fellow at CityUHK's Hong Kong Institute for Advanced Study.
This breakthrough resolves the longstanding issue of energy loss, allowing for high-performance nanoscale optical devices.
Dr. Liang Yao, Department of Electrical Engineering, City University of Hong Kong
The inverse square root law, a new universal law, has been found to demonstrate how plasmonic nanostructures' size can be changed to minimize energy loss drastically. This finding closes the gap between surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) and localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs), improving resonance quality in metal arrays by a factor of two.
This discovery creates intriguing opportunities for more robust light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Bridging high-loss localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) with low-loss surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) was a daunting problem that required novel thinking and a departure from standard methodologies.
This finding could completely change several industries, including solar energy, imaging, and sensing. By using this new method, scientists can create optical devices that are even more inventive and potent, leading to a new phase of technological progress.
Journal Reference:
Liang, Y., et al. (2024) From Local to Nonlocal High- Q Plasmonic Metasurfaces. Physical Review Letters. doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.133.053801.