According to a study published in Nature Nanotechnology, researchers at the University of Ottawa have made a significant advancement in the diagnosis of heart disease.
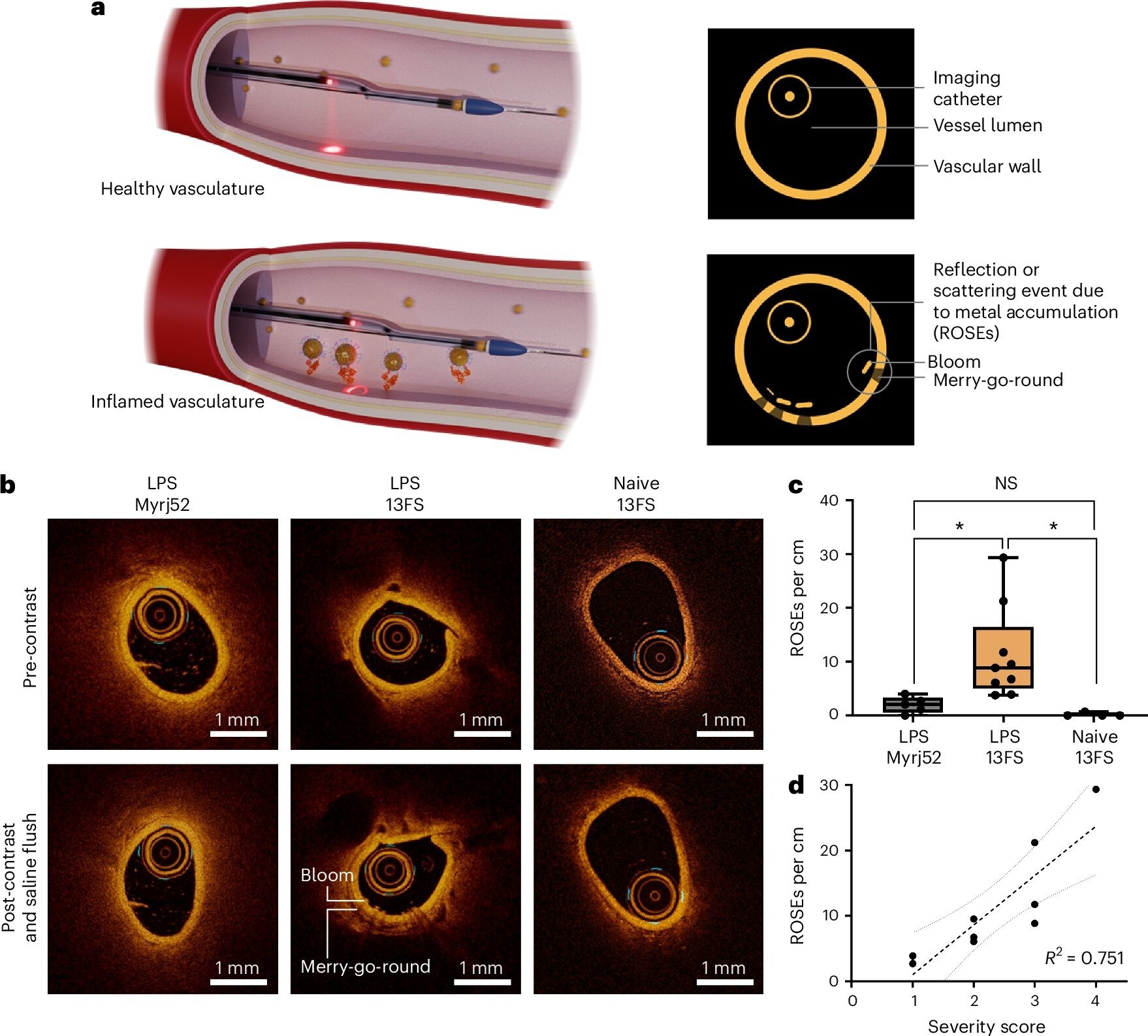 In vivo IV-OCT molecular imaging of intravascular inflammation with AuSC@(13FS)2. Image Credit: Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01802-2
In vivo IV-OCT molecular imaging of intravascular inflammation with AuSC@(13FS)2. Image Credit: Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01802-2
They have created a novel contrast agent for intravascular optical coherence tomography (IV-OCT), a medical imaging technique. The new agent, derived from gold superclusters (AuSC), could assist medical professionals in identifying heart conditions.
The research team developed these gold superclusters to work with the near-infrared light used in IV-OCT under the direction of Adam J. Shuhendler, Associate Professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Sciences at uOttawa. Due to their dense packing of gold nanoparticles, these superclusters improve the light scattering required for sharper imaging.
We have found a simple and quick way to produce these gold superclusters. We can also adjust them to make them perfect for improving IV-OCT imaging.
Adam J. Shuhendler, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Ottawa
The team applied a unique polymer to the gold superclusters to stabilize them and enable the attachment of targeting molecules.
This investigation focused on P-selectin, a sign of blood vessel inflammation. In laboratory tests, the novel contrast agent AuSC@(13FS)2 demonstrated strong binding to P-selectin, and in rats with inflammatory blood vessels, it enhanced IV-OCT imaging.
One of this new agent’s main advantages is its ability to provide comprehensive molecular information without altering the current IV-OCT protocols used in clinics. Like stents, the researchers discovered that AuSC@(13FS)2 produced clear reflections in the IV-OCT images when attached to inflammatory blood vessels.
Shuhendler added, “Our new contrast agent could lead to more personalized heart disease treatments. This technology might help doctors detect heart diseases earlier and assess the risk more accurately by providing detailed information about the blood vessels.”
Additionally, the study demonstrated a direct correlation between the quantity of P-selectin and the number of reflections observed in the images, indicating that this technique could be used to gauge the degree of inflammation. This study represents a significant advancement in the imaging and diagnosing heart disease. By enabling detailed imaging with IV-OCT, it provides new possibilities for early detection and individualized treatment of cardiac conditions.
Journal Reference:
Calvert, N. D. et. al. (2024) NIR-II scattering gold superclusters for intravascular optical coherence tomography molecular imaging. Nature Nanotechnology. doi.org/10.1038/s41565-024-01802-2