Oct 6 2009
Exploiting quantum mechanics for transmitting information is a tantalizing possibility because it promises secure, high speed communications. Unfortunately, the fragility of methods for storing and sending quantum information has so far frustrated the enterprise. Now a team of physicists in Sweden and Poland have shown that photons that encode data have strength in numbers. Their experiment is reported in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A and highlighted in the October 5 issue of Physics.
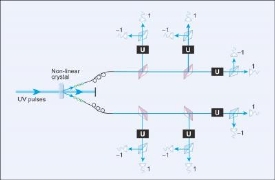 A new method for combining six photons together results in a highly robust qubit capable of transporting quantum information over long distances.
A new method for combining six photons together results in a highly robust qubit capable of transporting quantum information over long distances.
In classical communications, a bit can represent one of two states - either 0 or 1. But because photons are quantum mechanical objects, they can exist in multiple states at the same time. Photons can also be combined, in a process known as entanglement, to store a bit of quantum information (i.e. a qubit).
Unlike data stored in a computer or typically sent through conventional fiber optic cables, however, qubits are extremely fragile. A kink in a cable, the properties of the cable material, or even changes in temperature can corrupt a qubit and destroy the information it carries. But now a group lead by Magnus Rådmark at Stockholm University has shown that six entangled photons can encode information that stands up to some knocking around.
Rådmark and his team proved experimentally that their six photon qubits are robust and should be able to reliably carry information over long distances. The technology to encode useful information on the qubits and subsequently read it back is still lacking, but once those problems are solved, we will be well on our way to secure, reliable, and speedy quantum communication.
Also in Physics: Quasiparticles do the twist
Joel Moore writes a Viewpoint on a paper examining the experimental evidence for oddball particles that don't behave like either fermions or bosons, the two breeds of particles in quantum mechanics.