Nano-composites and polymer nano-films are utilized in a broad range of applications from packaging of food to sports equipment to aerospace and automotive applications. Thermal analysis is performed regularly in order to examine materials for these applications, but since nanostructured materials are being commonly used, bulk methods are not suitable.
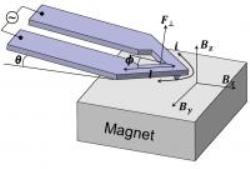 This is the atomic force microscope with an integrated heater actuated using Lorentz forces
This is the atomic force microscope with an integrated heater actuated using Lorentz forces
In order to determine temperature dependent material characteristics at the below-100 nm scale, nanoscale thermal analysis or nanoTA has been used in recent years. nanoTA is highly effective for soft polymers. Researchers at Anasys Instruments and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated that nanoTA can be performed on stiff materials such as filled composites and epoxies.
According to the College of Engineering Bliss Professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois, by this innovative method, it is possible to measure temperature as well as frequency-dependent material characteristics at a high-speed over a broad bandwidth. A current is made to flow around the U-shaped arms of the cantilever of a self-heating atomic force microscope (AFM) and the current is made to interact with a magnetic field. The tip-sample force is modulated near the AFM tip by the magnetic field.
According to the paper’s first author, Byeonghee Lee force control at the nanometer scale can be achieved, which is not dependent on the heating temperature.
According to co-author of the paper and CTO at Anasys Instruments, Craig Prater, traditional nanothermal analysis involved highly crosslinked, highly filled and below-100 nm thin films. This novel method has enabled consistent measurement and mapping of melting and glass transitions on material groups that were difficult before.
The paper is titled “Magnetic Actuation of a Heated Atomic Force Microscope Cantilever using Lorentz Force" and was published in the Nanotechnology journal.