May 21 2013
Waterproof fabrics that whisk away sweat could be the latest application of microfluidic technology developed by bioengineers at the University of California, Davis.
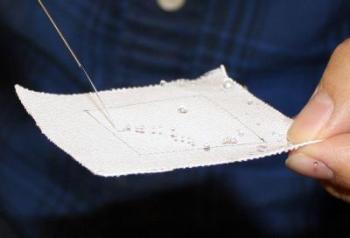 Water droplets are vigorously repelled by the fabric unless they are taken up by hydrophilic threads.. Credit: Holly Ober, UC Davis
Water droplets are vigorously repelled by the fabric unless they are taken up by hydrophilic threads.. Credit: Holly Ober, UC Davis
The new fabric works like human skin, forming excess sweat into droplets that drain away by themselves, said inventor Tingrui Pan, professor of biomedical engineering. One area of research in Pan's Micro-Nano Innovations Laboratory at UC Davis is a field known as microfluidics, which focuses on making "lab on a chip" devices that use tiny channels to manipulate fluids. Pan and his colleagues are developing such systems for applications like medical diagnostic tests.
Graduate students Siyuan Xing and Jia Jiang developed a new textile microfluidic platform using hydrophilic (water-attracting) threads stitched into a highly water-repellent fabric. They were able to create patterns of threads that suck droplets of water from one side of the fabric, propel them along the threads and expel them from the other side.
"We intentionally did not use any fancy microfabrication techniques so it is compatible with the textile manufacturing process and very easy to scale up," said Xing, lead graduate student on the project.
It's not just that the threads conduct water through capillary action. The water-repellent properties of the surrounding fabric also help drive water down the channels. Unlike conventional fabrics, the water-pumping effect keeps working even when the water-conducting fibers are completely saturated, because of the sustaining pressure gradient generated by the surface tension of droplets.
The rest of the fabric stays completely dry and breathable. By adjusting the pattern of water-conducting fibers and how they are stitched on each side of the fabric, the researchers can control where sweat is collected and where it drains away on the outside.
Workout enthusiasts, athletes and clothing manufacturers are all interested in fabrics that remove sweat and let the skin breathe. Cotton fibers, for example, wick away sweat — but during heavy exercise, cotton can get soaked, making it clingy and uncomfortable.
A paper describing the research was published recently in the journal Lab on a Chip. The work was funded in part by the National Science Foundation.