A recent review article published in the journal Nano Research Energy provides an overview of the evolution and synthesis of borophene. It discusses its applications in various sectors, such as energy harvesting, energy conversion, energy storage, sensors, and information storage.
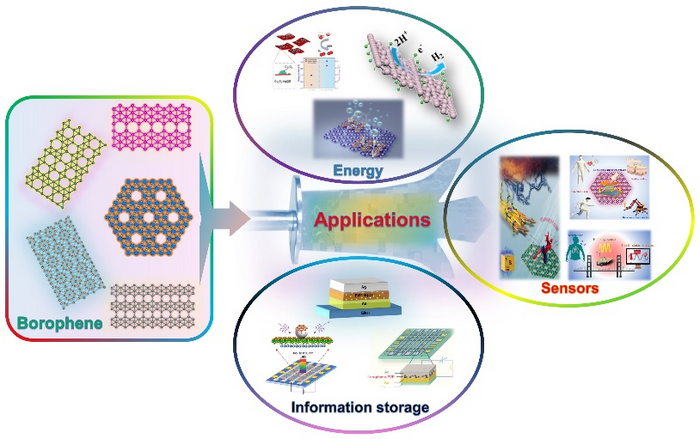
The 2D material borophene is comprised of a single element, making it ideal for applications in energy, sensors and information storage, according to a new review summarizing recent experimental developments. Nano Research Energy, Tsinghua University Press
Borophene: A Novel 2D Material with Promising Properties
The discovery of two-dimensional (2D) materials has opened up a new avenue for developing advanced technologies. These materials possess unique physical and chemical properties, making them promising candidates for various fields. However, their intrinsic limitations and shortcomings have hindered their full potential. This has led researchers to seek alternative materials with superior properties.
Borophene, a monoelemental 2D material with new characteristics, has appeared as an important material in many industrial applications. Among other characteristics, it has anisotropic plasmonics, physical compatibility, optical transmittance, ultrahigh thermal conductivity, and superconductivity.
Borophene has a broad bandgap range due to its many structural phases, making it a good choice for use as an insulator or sealing layer in semiconductors. In contrast to few-layered BP, certain common borophenes have shown high stability in ambient settings, even in acid or basic solvents.
Borophene is projected to advance as an electrode component for rechargeable lithium or sodium-ion batteries with better storage capacity than graphene.
With the experimental realization of stable and high-quality borophenes and their heterostructures in recent years, numerous research works have been experimentally reported for their applications in these fields.
Boron Synthesis: Challenges and Breakthroughs
Borophene as a 2D boron sheet was first reported in 1997. Since then, various stable 2D boron structures have been theorized, including α-sheet and β-sheet, which were found to be more stable than the initial structure.
To guide experimental realization, effective strategies were proposed, such as substrate support and surface passivation.
Synthesis of borophene has been achieved through CVD and MBE methods. However, borophene's instability in air has been a challenge, leading to the synthesis of stable borophene-based materials, such as hydrogenated borophene and borophene-based heterostructures.
“Borophene is a rising star monoelemental 2D material,” said Guoan Tai, co-author of the current review article.
Although many challenges exist in the experimental synthesis of borophene, it has made some exciting experimental progress in the fields of energy, sensing and information storage in recent years.
Guoan Tai, Co-Author
In 2020, a simple in-situ thermal decomposition method was proposed to prepare ultrastable, semiconducting, and high-quality hydrogenated borophene.
Importance of the Current Borophene Review
Borophene is a fascinating material that has been the subject of much research in recent years. Previous researchers have made great strides in understanding its properties and potential applications, and several literature reviews have been published on the topic.
However, most of these reviews have focused on the theoretical aspects of borophene and have not delved into its experimental developments for specific application fields, such as energy, sensors, and information storage.
The researchers, in this review, aimed to fill that gap by providing a comprehensive overview of recent experimental works on borophene-based materials. The paper includes a brief introduction to borophene evolution and synthesis as well as a detailed analysis of the latest research findings.
The authors also summarized the current state of borophene-based applications and provided insights into the challenges and opportunities that lay ahead for future research.
Applications and Future of Borophene-based Materials
Borophene-based materials have generated significant interest in recent years due to their unique electronic, thermal, and mechanical properties. These properties make them promising candidates for various applications, including energy storage, sensors, and information storage.
In the field of energy storage, borophene-based materials have demonstrated high theoretical capacity for storing lithium ions, making them suitable for use in lithium-ion batteries. The potential of these materials to provide high energy densities and fast charge/discharge rates make them promising for the development of next-generation energy storage devices.
Borophene-based materials also have potential applications in sensing technologies. Their high surface-to-volume ratio makes them attractive for gas sensing applications, with high sensitivity and selectivity for detecting trace amounts of gases.
Borophene-based materials also have potential applications in information storage, particularly in electronic and spintronic devices. Their high electron mobility and magnetic moment make them promising candidates for high-performance transistors and magnetic storage devices.
While much research is still needed to fully optimize the properties of borophene-based materials for these applications, their unique properties make them promising candidates for developing next-generation technologies.
Reference
Chuang, H. et al. (2023). Borophene-based materials for energy, sensors and information storage applications. Nano Research Energy. Available at: https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2023.9120051
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.
Source:
: Tsinghua University Press