Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer with a high mortality rate once it metastasizes. Localized chemotherapy is typically an option only in the early stages (in situ melanoma) or as a postoperative treatment following surgical removal of suspicious lesions. Drugs such as Imiquimod, 5-Fluorouracil, Dacarbazine, and Doxorubicin have been tested for this purpose, showing promising effects. More recently, researchers have been exploring the potential of metal nanoparticles, both as standalone treatments and as drug carriers.
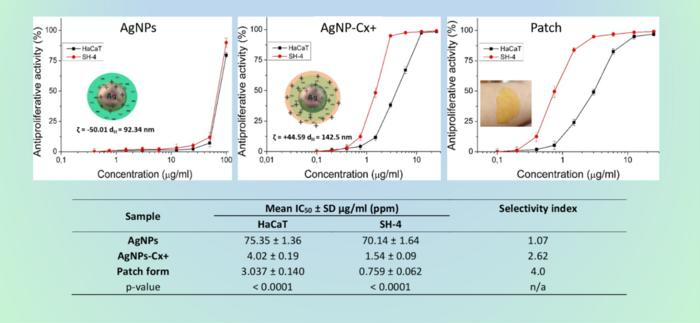
Anti-tumor activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and chlorhexidine-silver nanoparticles conjugates (AgNP-Cx+) against melanoma. Legend: ζ-zeta potential – characterizes the charge of the silver nanoparticles; dH hydrodynamic diameter – the size that the particles acquire in an aqueous dispersion; HaCaT – normal cells, human keratinocytes; SH-4 – tumor cells, human melanoma; IC50 – the concentration that inhibits cell proliferation at 50%; SD – standard deviation of the values based on six repetitions of the experiment; ppm – part per million; Selectivity Index – an index that is calculated as the quotient of IC50 on normal cells and IC50 on tumor cells; the greater its value, the more selective the agent against the cancer cells; p-value – statistical indicator; the lower the value the greater the statistical significance between the results obtained with the different samples; a borderline for significance is normally set at p<0.05; n/a – not applicable. Image Credit: Nadezhda Ivanova
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have gained particular attention in nanomedicine, drug delivery, and theranostics due to their broad antimicrobial and anti-tumor properties. Their pharmacological effects, however, are closely tied to their "surface functionality."
Studies suggest that negatively charged, spherical AgNPs are generally less toxic than their positively charged or irregularly shaped counterparts (such as rods or wires). However, this reduced toxicity also means they tend to be less effective as anti-cancer agents.
Modern pharmaceutical development increasingly emphasizes eco-friendly, or "green," technologies that eliminate the need for toxic solvents and reagents. This study utilized one such approach, employing Camellia sinensis (green tea leaves) as a natural reducing agent for silver ions.
To enhance both antimicrobial and anti-tumor activity, the AgNPs were further conjugated with chlorhexidine (Cx+), a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent and cationic surfactant. The results were striking: the AgNP-Cx+ complexes demonstrated significantly stronger antimicrobial properties, an 18-fold increase in anti-melanoma activity, and three times greater tumor selectivity compared to non-functionalized AgNPs.
Perhaps the most significant outcome of this research, recently published in Pharmacia, was the development of an adhesive patch prototype for topical application of the AgNP-Cx+ complex. The chosen polymers—Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and Eudragit® RS—did not interfere with the antiproliferative action of the active agent. In fact, they helped double its activity while improving tumor selectivity even further.
Journal Reference:
Ivanova, N. A., et. al. (2025) Anti-melanoma activity of green-produced nanosilver-chlorhexidine complex. Pharmacia. doi.org/10.3897/pharmacia.72.e143419