Apr 7 2009
In 2007 and 2008 two groups of theoretical physicists (Hammer and Platter, and von Stecher, D'Incao, and Greene) predicted the existence of universal four-body states that are closely tied to Efimov trimer states. Now, a team of scientists of the Institute for Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck, Austria, has proven these states experimentally in an ultracold gas of cesium atoms. At particular energy separations from an Efimov state, they found two four-body loss resonances, which are a strong evidence for the existence of a pair of four-body states closely tied to Efimov trimers. "Ultracold atomic clouds provide a very good system to study these few-body phenomena in experiments", Francesca Ferlaino says, "because we are able to accurately control the interaction conditions and, thus, the separation between the particles."
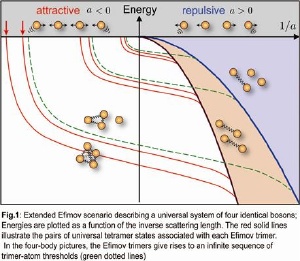 Extended Efimov scenario describing a universal system of four identical bosons; Energies are plotted as a function of the inverse scattering length. The red solid lines illustrate the pairs of universal tetramer states associated with each Efimov trimer. In the four-body pictures, the Efimov trimers give rises to an infinite sequence of trimer-atom thresholds (green dotted lines). Picture: Jose D'Incao
Extended Efimov scenario describing a universal system of four identical bosons; Energies are plotted as a function of the inverse scattering length. The red solid lines illustrate the pairs of universal tetramer states associated with each Efimov trimer. In the four-body pictures, the Efimov trimers give rises to an infinite sequence of trimer-atom thresholds (green dotted lines). Picture: Jose D'Incao
Few-body problems are among the most difficult ones in physics and for centuries the cleverest minds have been engaged in looking for solutions to the problems that arise in this field. Today it takes comprehensive experiments and an enormous numerical computing effort to solve the problems. The scientific world has now made an important step towards finding simple laws for the complex relations between several interacting objects.
The starting point was the discovery of the Russian physicist Vitali Efimov at the beginning of the 1970s, who predicted the existence of an infinite series of universal three-body quantum states. One of the remarkable properties is the fact that three particles bind to form a weakly bound entity – a trimer - while a dimer of the same particles is not formed. In 2006, 35 years after Efimov presented his paradigm, scientists led by Rudolf Grimm succeeded in proving the phenomenon experimentally and the research on Efimov states has now become a field of research in its own right in the physics of ultracold atoms.
The Innsbruck scientists report on their findings in the journal Physical Review Letters. The project is supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF). The successful Italian physicist Francesca Ferlaino, who has worked as a junior scientist in Rudolf Grimm's group for three years, is supported by the Lise-Meitner program of the Austrian Science Fund. She has started to establish her own research group at the Institute for Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck.
http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.140401