Jul 15 2009
Fuel cells can compete with batteries, the internal combustion engine and the power grid. Hydrogen can compete with any fuel now produced and cause no pollution but its price is higher than gasoline or natural gas because it is difficult to transport and store. Nanotechnologies will provide the technological keys that enable fuel cells and hydrogen as a fuel to become competitive and commonplace. iRAP has published a new directory with profiles over 800 companies and institutions in fuel cells, hydrogen energy and related nanotechnologies.
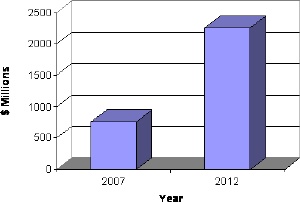
As noted in the report, more than 3870 organizations are involved in fuel cells, hydrogen energy and related nanotechnology and spent an estimated $8.4 billion in 2008. This market is estimated at $8.8 billion in 2009 and expected to increase to $14 billion by 2014, with a compound average growth rate of 9.6%. More than 2180 organizations are involved in nanotechnology related to fuel cells and hydrogen energy and will spend a total of $4.7 billion for fuel cells and hydrogen energy incorporating nanotechnology. Of that $4.7 billion, about $2 billion in 2008 represents the value of nanotechnology for fuel cells and hydrogen energy separate from all other expenditures.
The organizations are made up of well established corporations, start-up companies, universities, governments at the federal, state and municipal level, cooperative public/private demonstrations, as well as non-profit organizations and laboratories.
This directory provides profiles companies, government organizations and universities involved in commercializing fuel cells, hydrogen energy and related nanotechnology. The information is drawn from their websites, press releases, media stories, annual reports, conference presentations, filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and reports to the U.S. Department of Energy and other Federal Agencies as well as reports to various U.S. states and reports to various agencies in European and Asian governments. Some profiles are the result of foreign language translations of public information. Languages from which some profiles were translated include: French, German, Italian, Polish, Spanish, Swedish, Russian, Chinese, Japanese and Korean.
The companies and organizations profiles were selected for their leadership positions in sales and technology related to fuel cells, hydrogen energy and related nanotechnology and those companies that are major material providers to the fuel cell industry. Companies and organizations were also chosen for their nanotechnology contributions to the fuel cell and hydrogen energy industries.
The directory is divided into four broad sections. The first section covers companies primarily involved in proton exchange fuel cells (PEMFC), direct methanol fuel cells (DMFC) and other low temperature fuel cells. The second section covers high temperature fuel cell companies involved in solid oxide fuel cells, molten carbonate fuel cells and phosphoric acid fuel cells. The third section provides profiles of companies involved in provide hydrogen and other fuels for fuel cells. The fourth section covers other companies such as those who provide balance of plant apparatus and materials. This section is the smallest as the focus is on those companies with involvement in both nanotechnology for fuel cells or hydrogen energy.
Within each section the companies are arranged in alphabetical order with a brief subtitled following the company or organization name to provide, at a glance, their chief activity with regard to fuel cells, hydrogen energy and related nanotechnology. Organization addresses, telephone and fax numbers, email contact and website URL are provided for most of the companies.