Jul 21 2009
To understand transformations of matter, scientists at DOE's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory aided in developing methods to determine how fast clusters of molecules form and their corresponding stability.
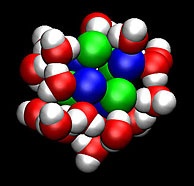 Scientists developed methods to
determine how fast clusters of
molecules, such as this salt and
water cluster, form and their
corresponding stability.
Scientists developed methods to
determine how fast clusters of
molecules, such as this salt and
water cluster, form and their
corresponding stability.
Molecular-level reactions that produce aqueous nanoparticles ultimately aid in designing better crystals for manufacturers and new catalysts for producing alternative fuels. The PNNL-led team designed new theoretical and computational approaches to studying the nanoparticle formation. With the new approach, the team determined the rate constants, or how fast the clusters dissociated or fell apart. Next, they determined the thermodynamic stability of the clusters, and provided a streamlined approach to calculate cluster thermodynamics. Key research was done at DOE's EMSL, a national scientific user facility.
Source: Oak Ridge National Laboratory