Scientists have leaped over a major hurdle in efforts to begin commercial production of a form of carbon that could rival silicon in its potential for revolutionizing electronics devices ranging from supercomputers to cell phones. Called graphene, the material consists of a layer of graphite 50,000 times thinner than a human hair with unique electronic properties. Their study appears in ACS' Nano Letters, a monthly journal.
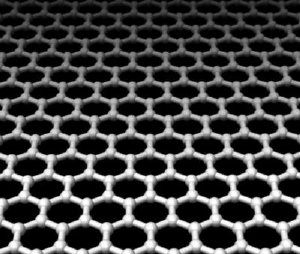 Scientists have developed a simple, inexpensive manufacturing method that could allow mass production of graphene (illustrated above) for electronics applications. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Scientists have developed a simple, inexpensive manufacturing method that could allow mass production of graphene (illustrated above) for electronics applications. Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Victor Aristov and colleagues indicate that graphene has the potential to replace silicon in high-speed computer processors and other devices. Standing in the way, however, are today's cumbersome, expensive production methods, which result in poor-quality graphene and are not practical for industrial scale applications.
Aristov and colleagues report that they have developed "a very simple procedure for making graphene on the cheap." They describe growing high-quality graphene on the surface of commercially available silicon carbide wafers to produce material with excellent electronic properties. It "represents a huge step toward technological application of this material as the synthesis is compatible with industrial mass production," their report notes.
ARTICLE FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
"Graphene Synthesis on Cubic SiC/Si Wafers. Perspectives for Mass Production of Graphene-Based Electronic Devices"
DOWNLOAD FULL TEXT ARTICLE
http://pubs.acs.org/stoken/presspac/presspac/full/10.1021/nl904115h