mPhase Technologies has devised a smart surface technology that uses the electrowetting phenomenon or the capability to electronically control the behavior of liquids during their contact with a porous or solid surface.
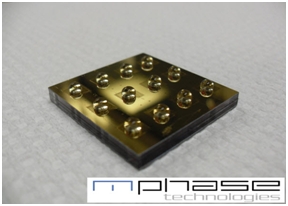 Smart material surface made from silicon wafer. Water droplets repelled from going through the pores of the silicon membrane due to superhydrophobic properties of the silicon surface.
Smart material surface made from silicon wafer. Water droplets repelled from going through the pores of the silicon membrane due to superhydrophobic properties of the silicon surface.
Liquids such as an organic liquid will bead up on a superlyophobic surface, but can be made to travel or spread out using electrowetting phenomenon. Water behaves in the same way on a superhydrophobic surface. The innovative smart surface technology is being employed to form ‘smart’ patterns on polymer, ceramic, metal surfaces and other novel materials that can prevent forming ice, fogging up and getting dirty. It can also be utilized for lenses, displays and much more.
mPhase Technologies is currently working on the development of its Smart NanoBattery by directing the liquid electrolyte using the electrowetting phenomenon through its proprietary porous silicon structure. The innovation leads to a novel reserve-style battery design that can be used in a broad array of chemistries such as zinc manganese dioxide chemistries, which resemble the standard alkaline battery utilized in television remote control and flashlight, and lithium manganese dioxide-based high-energy density chemistries used in digital cameras, mobile phones and laptops. Lithium-based chemistries used in rechargeable batteries can also be developed using the battery novel design.
mPhase Technologies plans to introduce and prove the novel smart surface technology first for a reserve battery, then for a primary cell made of zinc manganese dioxide or lithium manganese dioxide chemistries, and finally a rechargeable or secondary battery. If produced, the mPhase battery family comprising reserve, primary and secondary batteries find use in a broad array of applications.