May 17 2013
Nanomaterials exhibit unique properties that can only unfold when the structures of the material are very small – that is, at the nanoscale. In order to exploit these special properties such as, for example, specific quantum effects it is very important to produce predefined nanostructures in a controlled way and interpret the formation of their shape.
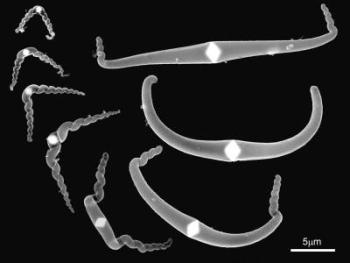 The unique shape of the carbon nanomustaches -- one of the few inorganic examples that researchers achieved to grow and control and where they observed bilateral formation- is captured under an electron microscope. Credit: Copyright: Shiozawa/EMP, University of Vienna
The unique shape of the carbon nanomustaches -- one of the few inorganic examples that researchers achieved to grow and control and where they observed bilateral formation- is captured under an electron microscope. Credit: Copyright: Shiozawa/EMP, University of Vienna
Scientists try to understand how to initiate and control the growth of nanomaterials and are exploring different ways to design and build up nanostructures with fine control over shapes. In nature, many organic forms grow bilaterally, that is, symmetrically in two distinct directions. An international team of researchers from the University of Vienna (Austria), the University of Surrey (UK) and the IFW Dresden (Germany) have now achieved such a bilateral formation of inorganic nanomaterials in a controlled environment by implementing a new method.
How to grow a nanomoustache
The scientists pressurized a gas consisting of carbon and iron atoms at an elevated temperature until they observed two arms of carbon atoms spontaneously started growing out of an iron core. When the iron core was small enough, the two carbon arms started spiraling at their ends so that the whole nanostructure bore a striking resemblance with a twirled moustache. "The encouraging insights we gained from our experiments provide a very good starting point for the controlled production of extraordinary new materials with designed nanostructures", expects Dr. Hidetsugu Shiozawa, leading author of the scientific publication and researcher at the Faculty of Physics at the University of Vienna.
Useful imperfections
In order to find out more about the internal architecture of the nanomoustaches, the researchers cut their nanomaterial into extremely thin slices and used a special microscopy technique – the transmission electron microscopy – to have a closer look at the slices. When nanostructures grow, structural imperfections of the material emerge that are characteristic for the way the material was formed. In the observed herringbone pattern of the sliced nanomoustache, the distribution of the structural imperfections allowed the scientists to look back in time and extract further information about the formation of the nanomaterial. For future applications it will be fundamental to apply their knowledge to the growth of nanostructures in 2 or 3 dimensions in order to build regular patterns and networks at the nanoscale. Therefore, the scientists strive to understand even more about the mechanism behind the formation pattern of the nanomoustaches and are aiming at growing more dimensional and more complex nanostructures in future research projects.