Jan 27 2015
A study led by the National University of Singapore (NUS) found that attaching chemotherapy drug Epirubicin to nanodiamonds effectively eliminates chemoresistant cancer stem cells. The findings were first published online in ACS Nano, the official journal of the American Chemical Society, in December 2014.
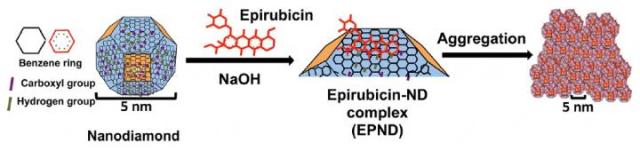 This is a schematic model showing surface and chemical structure of nanodiamond (ND) and Epirubicin (Epi), synthesis and aggregation of Epirubicin-ND complex (EPND). ND represented in truncated octahedron structure with different surface charge denoted with color. ND surface functional group indicated, including benzene ring, carboxyl group and hydrogen group. Molecular skeleton representing carbon, oxygen and Nitrogen atoms in Epi molecule was shown in red. Credit: National University of Singapore
This is a schematic model showing surface and chemical structure of nanodiamond (ND) and Epirubicin (Epi), synthesis and aggregation of Epirubicin-ND complex (EPND). ND represented in truncated octahedron structure with different surface charge denoted with color. ND surface functional group indicated, including benzene ring, carboxyl group and hydrogen group. Molecular skeleton representing carbon, oxygen and Nitrogen atoms in Epi molecule was shown in red. Credit: National University of Singapore
The research team, led by Assistant Professor Edward Chow, Junior Principal Investigator at the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at NUS, demonstrated the use of nanotechnology to repurpose existing chemotherapy drugs as effective agents against chemoresistant cancer stem cells. Chemoresistance, which is the ability of cancer cells to escape chemotherapy treatment, is a primary cause of treatment failure in cancer. Cancer stem cells, a type of cancer cell which initiates the formation of tumours, are commonly found to be more resistant to chemotherapy than the rest of the bulk tumour, which can lead to cancer recurrence following chemotherapy treatment. As such, there is intense interest in developing new drugs or treatment strategies that overcome chemoresistance, particularly in cancer stem cells.
In this study, widely-used chemotherapy drug Epirubicin was attached to nanodiamonds, carbon structures with a diameter of about five nanometres, to develop a nanodiamond-Epirubicin drug delivery complex (EPND). The researchers found that while both standard Epirubicin as well as EPND were capable of killing normal cancer cells, only EPND was capable of killing chemoresistant cancer stem cells and preventing secondary tumour formation in xenograft models of liver cancer.
Compared to other approaches such as combinatorial therapy of chemotherapy drugs with inhibitors of chemoresistance pathways, delivery of existing chemotherapy drugs with nanomaterials, in this case nanodiamonds, provide a broader range of protection in a package that is both safer and more effective. The study showed that delivery of Epirubicin by nanodiamonds resulted in a normally lethal dosage of Epirubicin becoming a safe and effective dosage. As such, delivery of chemotherapy drugs by nanodiamonds not only enables enhanced killing of chemoresistant cancer stem cells, but may be a useful alternative for patients who cannot tolerate the toxic side effects of standard chemotherapy drugs.
Furthermore, the versatility of the nanodiamond-based drug delivery platform opens up the possibility of future applications of nanodiamonds such as the addition of other similar drugs as well as active targeting components such as antibodies or peptides against tumour cell surface proteins for targeted drug release. In addition, the application of a nanodiamond-drug delivery system is not limited to liver cancer. It offers a promising approach to treating a broad range of difficult cancers, particularly those driven by chemoresistant cancer stem cells.
In collaboration with Professor Dean Ho at the University of California Los Angeles and Professor Li Jianzhong at Peking University, Asst Prof Chow's group is working towards completing preclinical work on anthracycline delivery by nanodiamonds and hope to begin clinical trials in the near future.