Oct 15 2015
Totally internal confined whispering-gallery modes can have high Q factors in wavelength scale optical microresonators, such as microspheres and two-dimensional microdisk resonators. Square optical resonators can also support high Q whispering-gallery modes, suitable to realize unidirectional microlasers.
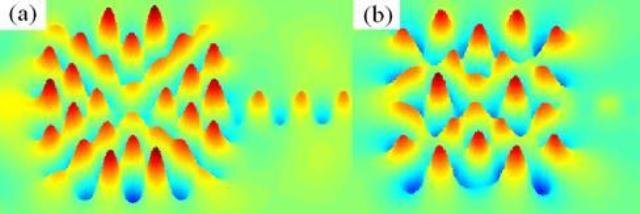 Mode field patterns for a square resonator with a side length of 2.5 ìm connected with a waveguide. Credit: ©Science China Press
Mode field patterns for a square resonator with a side length of 2.5 ìm connected with a waveguide. Credit: ©Science China Press
Microsquare lasers have a larger overlap between the mode field pattern and injected carriers than microdisk lasers, which can result in better high-speed modulation behaviors. In addition, microsquare lasers can have higher slope efficiency and output power than microdisk lasers, due to the more evenly distributed mode field.
For a square optical microresonator, the mode field patterns around the perimeter exhibits the longitudinal and transverse mode field distributions. So the mode Q factors are greatly influenced by connecting an output waveguide to the resonator. The fundamental transverse mode with field pattern in Fig. 1(a) has a very small mode Q factor due to its strongly coupling to the output waveguide, and the first order transverse mode in Fig. 1(b) has a high Q factor.
Mode selection in square resonator microlasers is demonstrated by adjusting the width of the output waveguide coupled to the midpoint of one side. Through adjusting the width of the output waveguide, the mode interval of the high-Q modes can reach four times of the longitudinal mode interval. Therefore, mode hopping can be efficiently avoided and the lasing wavelength can be tuned continuously by tuning the injection current. For a 17.8-μm-side-length square microlaser with a 1.4-μm-width output waveguide, mode-hopping-free single-mode operation is achieved with a continuous tuning range of 9.2 nm.
Furthermore, dual-transverse-mode microsquare lasers with a tunable wavelength interval are designed and fabricated by using a square-ring patterned contact window. For the microsquare laser with the side length of 30 μm, the wavelength interval increases from 0.25 to 0.37 nm with the intensity ratio less than 2.5 dB as the injection current increases from 89 to 108 mA.