The rapid growth of research on 2-D materials – materials such as graphene and others that are a single or few atoms thick – is fueled by the hope of developing better performing sensors for health and environment, more economical solar energy, and higher performing and more energy efficient electronics than is possible with current silicon electronics.
Technical roadmaps, such as the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS), first published in 1998, serve as guides for future advances in a particular field and provide a means for organizations to plan for investments in new technology.
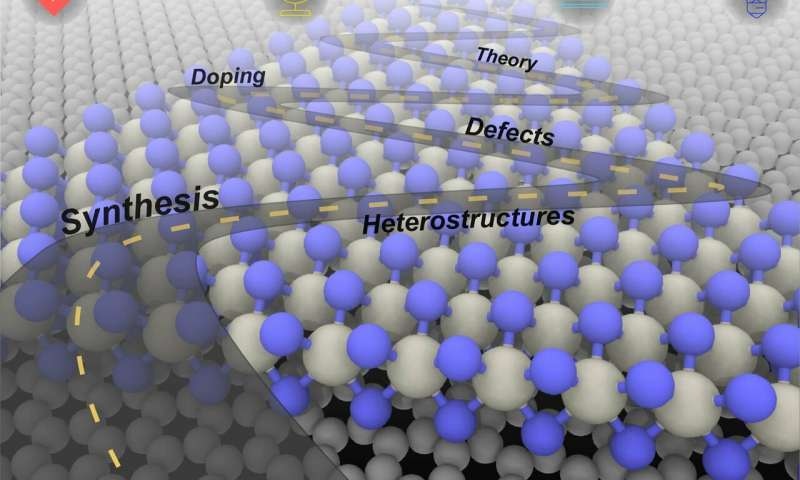
An invited article in the December online edition of the journal 2-D Materials provides a roadmap for the synthesis of electronic-grade two-dimensional materials for future electronic and sensing applications. Led by Penn State, with contributions from five additional universities and national laboratories, the roadmap addresses the grand challenges in 2-D materials with useful electronic or photonic properties, and the outlook for U.S. advances in the field.
 "This article is a review of where we currently are in regard to the synthesis of 2-D materials and our thoughts on the top research priorities that need to be addressed to achieve electronic grade 2-D materials," said Joshua Robinson, associate professor of materials science and engineering, whose Ph.D. students Natalie Briggs and Shruti Subramanian are co-lead authors on the report titled "A Roadmap for Electronic Grade 2-Dimensional Materials," published online today, Jan. 17.
"This article is a review of where we currently are in regard to the synthesis of 2-D materials and our thoughts on the top research priorities that need to be addressed to achieve electronic grade 2-D materials," said Joshua Robinson, associate professor of materials science and engineering, whose Ph.D. students Natalie Briggs and Shruti Subramanian are co-lead authors on the report titled "A Roadmap for Electronic Grade 2-Dimensional Materials," published online today, Jan. 17.
The authors divided the paper into four parts: Grand Challenges, which are the technology drivers, such as the internet of things; Synthesis, the techniques and theories required to grow close to perfect 2-D materials; Materials Engineering, which is fine tuning the properties of 2-D and composite materials; and finally, Outlook, which is the future of electronic devices when silicon technology reaches an inevitable roadblock.
"To put our roadmap together, we reached out to experts in various subfields, such as different synthesis approaches, defect engineering and computational theory," said Briggs of the two-year project. "We asked them to talk about the key fundamental challenges and the steps required to address these challenges in their area of expertise."
Robinson added, "This is the first roadmap focused on 2-D synthesis for electronic applications and there are still a lot of open questions. We want to bring some of those topics into the light."
A list of the twenty authors and their affiliations can be found online in the open access article in 2-D Materials.