New findings of nanotechnology in Agriculture in post-harvest loss reduction and food processing and was written in the journal Heliyon. Nanotechnology is among the promising techniques that might boost agricultural output by developing nano fertilizers, using more effective herbicides and pesticides, regulating soil features, managing wastewater, and detecting pathogens.

Study: Application of nanotechnology in agriculture, postharvest loss reduction and food processing: food security implication and challenges. Image Credit: Fotokostic/Shutterstock.com
Food Security in Underdeveloped Nations
Due to low agricultural production, deterioration of environmental assets, substantial post-farm losses, little or no quality enhancement, and fast population increase, ensuring food security in underdeveloped nations is extremely difficult. Researchers are attempting to incorporate modern technology to increase supply and close the gap between supply and demand for food.
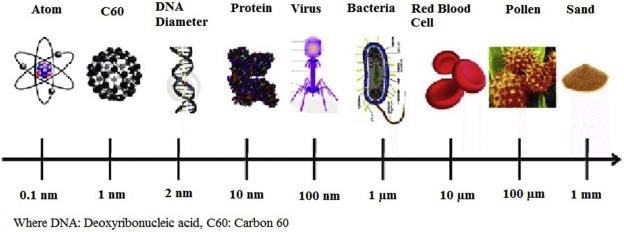
A pictorial exhibition of things in the “nano” (<100 nm) and “micro” (>100 nm) size ranges. Where DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, C60: Carbon 60. Image Credit: Neme, K., et al
Farmers all across the world will focus on boosting crop yield through intense and extended agriculture by incorporating new ideas and technology. Precision farming and the usage of nano-modified stimulants have increased current efforts.
The Need to Develop New Technologies
Developing new technologies is critical to enhancing agricultural output while reducing food waste to preserve new sustainability standards and improve food and nutrition security. Nanotechnology has the potential to provide foods of exceptional quality in a highly practical form while also increasing nutritional bioavailability.
Agriculture is regarded by most developing countries as the backbone of their economies, and it plays a critical part in their advancement and prosperity. As populations continue to grow, meeting higher supply demands is a key focus of innovative agricultural technologies.
Nanotechnology as the Answer
There are several uses of nanotechnology in agribusiness, including wastewater treatment, improving the quality of contaminated soil, and increasing agricultural output via security in the form of disease detection sensors.
Nanobiosensors, for example, are a wide range of nanotools that support the development of high-tech agricultural farms while also demonstrating the practical and planned uses of nanotools in case of crop control input and management accuracy.
Nano-forms of silica, carbon, silver, and alumino-silicates are among the nanoparticles used to detect plant diseases. It is recommended that the use of nanomaterials in agriculture decrease spraying pesticides by ensuring a steady supply of energetic molecules. It can reduce nutrient waste during fertilizer application and increase harvests by improving water and ingredient administration.
Nanotechnology also enabled gene sequencing, which increased the identification and application of plant characteristics, adjusting their ability to adapt to environmental stresses and illnesses.
Nanoemulsions reduce the need for stabilizers by protecting food from breaking and splitting, resulting in a significant reduction in the quantity of fat required. Several nanoemulsions appear to be optically transparent and have a number of technical benefits when it comes to mixing liquids. Nanoemulsions' end products are highly creamy, just like regular food items, with no alterations in mouthfeel or flavor.
Challenges in Agricultural Nanotechnology
As previously mentioned, nanotechnology is widely employed for food and agricultural purposes. Nanomaterials, on the other hand, are linked to a slew of safety concerns, owing to the possibility of their risk values infiltrating cells due to their small sizes and lingering in the system.
Because of many antagonistic effects of distinct nanoparticles, the increased use of nanotechnology in agricultural operations and food products is of great concern to a large portion of society. Environmental circumstances can cause nanocomposites to degrade, resulting in the release of incorporated nanoparticles from polymeric textures into the environment.
Herbicides and nano fertilizers are employed in agriculture and are distributed into the water, soil, and environment, posing a serious health risk to farmers. Plant development is likely to be hampered by the buildup of nanoparticles in the soil, eventually concentrating in edible tissues.
Benefit of Nanotechnology
The remarkable phenomenon of nanoparticles and nanostructures improving different attributes due to their tiny size, higher surface area, and highly catalytic nature has been noticed via multiple study discoveries.
Nanotechnology plays a critical role in ensuring food security, particularly in agriculture. It has the potential to boost crop yield by providing effective microbial, insect, and weed management that is high in economic value, protection, and safety. It also helps with food processing, food customization, stability, detecting, shelf life extension, food loss reduction, and food safety. With improved stability, safety, and packing material, nanotechnology can also reduce post-harvest losses.
Continue reading: How Agricultural Nanotechnology Will Influence the Future of Farming Sustainability.
Reference
Neme, K., Nafady, A., Uddin, S. and Tola, Y., (2021) Application of nanotechnology in agriculture, postharvest loss reduction and food processing: food security implication and challenges. Heliyon, 7(12), p.e08539.n. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08539
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.