Reviewed by Mila PereraNov 2 2022
FDA-approved iron oxide nanocrystals (IONs) as negative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents are experiencing obstacles due to their low relaxation rate and coherent ferromagnetism. Though metal doping has been discovered to be an effective method of improving the magnetic property and MRI contrast performance, the systemic mechanism has rarely been discussed.
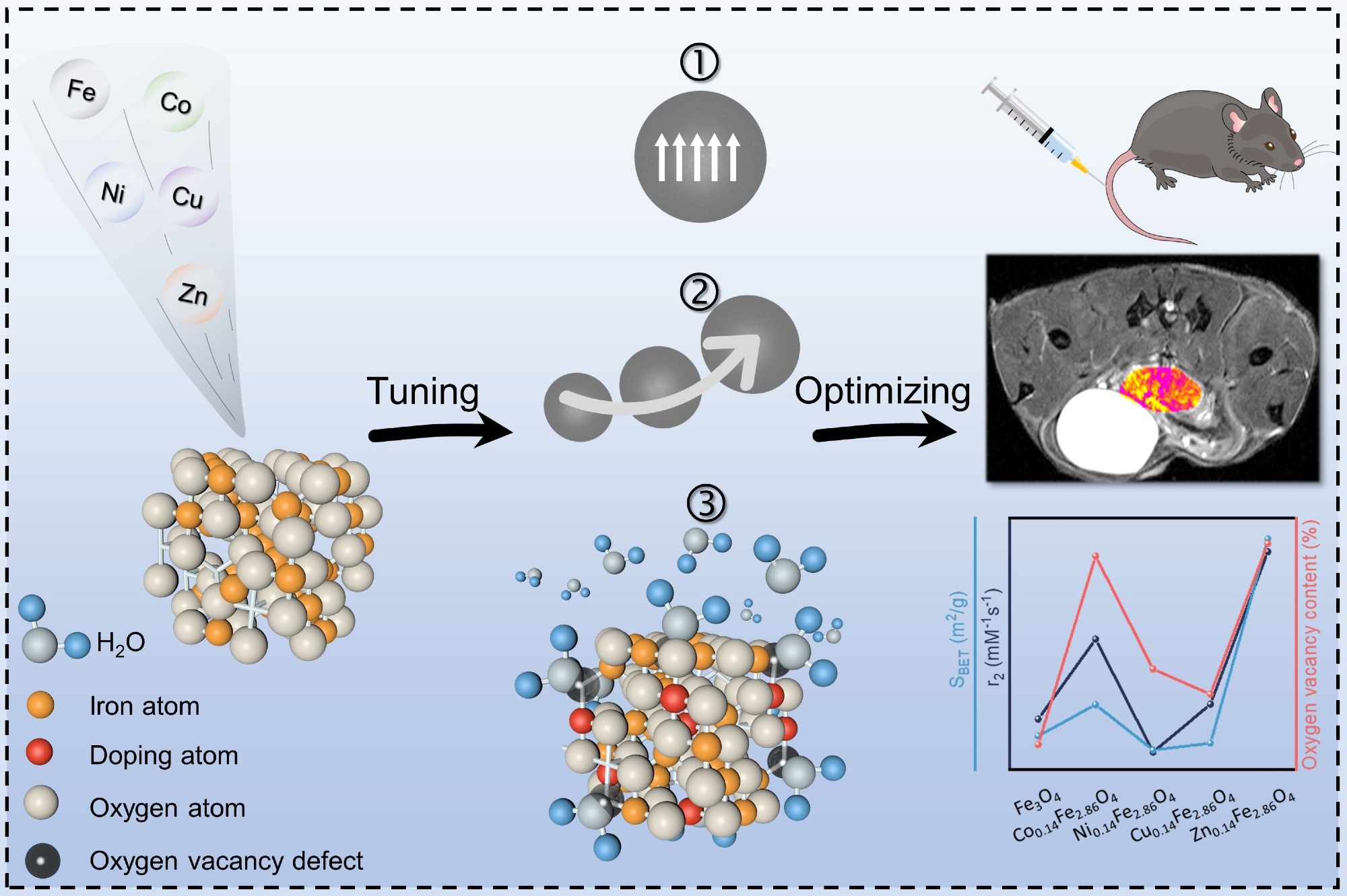
Schematic illustration. Image Credit: Wenteng Xie.
Investigators headed by Prof. Zhengyan Wu from the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) and scientists from Binzhou Medical University created a series of transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals and systematically investigated the mechanism of doping behavior on the magnetic resonance contrast performance of iron oxide nanocrystals.
The discovery, published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry B, establishes a new reference and foundation for the development of excellent magnetic resonance contrast agents.
In this investigation, the researchers used a simple thermal degradation method to create a series of hydrophilic transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals. They thoroughly investigated the changes in their physicochemical properties, disclosing the mechanism of the improved magnetic resonance signal of the transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals.
Thereafter, the optimal sample group was chosen to test the amplification of magnetic resonance signals in an in situ prostate cancer mouse model.
This study demonstrates the mechanism of magnetic resonance signal enhancement of transition metal-doped iron oxide nanocrystals, providing new insight into the development of efficient magnetic resonance contrast agents.
The Taishan Scholars Construction Engineering, the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Plan for Anhui Major Provincial Science and Technology Project funded the study.
Journal Reference
Xie, W., et al. (2022) Transition metal doped hydrophilic ultrasmall iron oxide modulate MRI contrast performance for accurate diagnosis of orthotopic prostate cancer. Journal of Materials Chemistry B. doi.org/10.1039/D2TB01860H.