Image Credit: Fishman64/Shutterstock.com
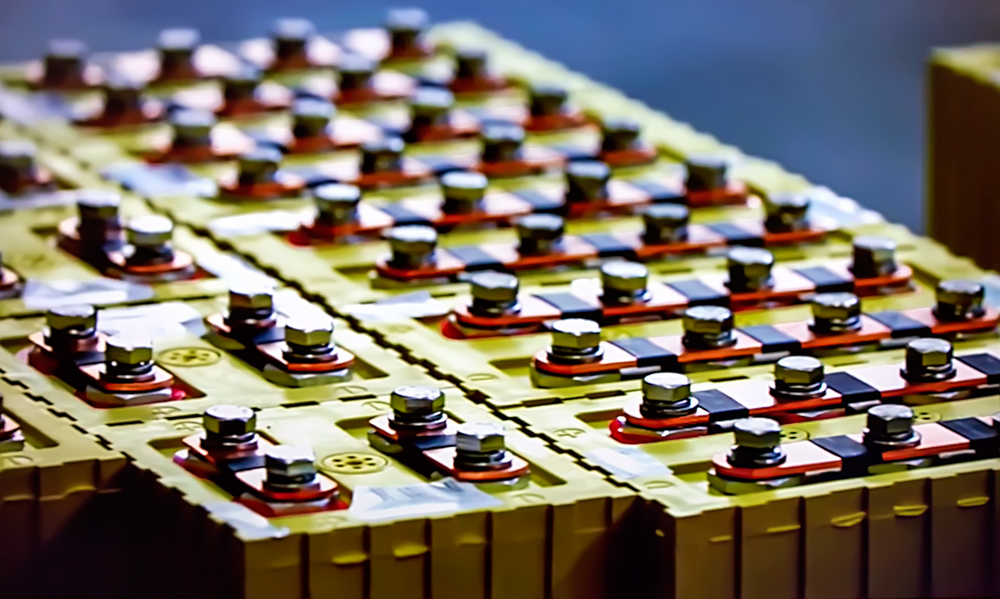
Nanotech Energy is developing a new generation of graphene lithium batteries with superior performance to those currently on the market. The batteries are expected to replace the traditional lithium-ion battery and feature revolutionary energy storage abilities. They find many applications in the modern world, such as electric vehicles.
Since lithium-ion batteries entered the market in 1991, they have revolutionized people’s lives. Their significance was acknowledged in 2019 when John B. Goodenough, M. Stanley Whittingham, and Akira Yoshino were awarded the Nobel Prize in chemistry for their development.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used power source worldwide for portable electronics. However, the battery industry's advancement has not been as rapid as the electronics industry, which has progressed significantly in the past decade, following Moore’s Law.
Moore’s law states that transistor sizes are decreasing exponentially with time. However, the power consumed by each transistor does not fall proportionally to the size. With the large power needed for electronic devices, the battery industry's development that Nanotech Energy is proposing is crucial to portable electronics.
About Nanotech Energy
Nanotech Energy was created in 2014 to revolutionize the battery industry and the way portable electronic devices are powered. The company’s research focuses on developing and producing graphene-based energy storage devices to bring them to the market.
Why is Graphene Important in Today’s Industries?
Graphene is a two-dimensional material consisting of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. It was first isolated in 2004 by Professor Sir Andre Geim and Professor Sir Kostya Novoselov. Many scientists believe that graphene is one of the most important materials available to modern science due to its extraordinary physical and electrical properties.
Graphene’s exceptional electrical properties include high conductivity, high charge carrier mobility, and low resistance. These properties are essential for batteries' performance – for example, if a high conductivity material is used in batteries, it prevents them from overheating.
Graphene-Based Batteries
The Graphene SuperBattery being developed by Nanotech Energy has many key advantages: safety, efficiency, fast charging, and long-lasting. They are also highly customizable and find applications in devices that need high energy or high power.
The Super Battery has low internal resistance, allowing high-speed charging. According to Nanotech Energy, the battery charges 18 times faster than current batteries available on the market.
The company is currently working on two types of graphene lithium batteries – Gen I graphene super batteries and Gen II graphene super batteries.
Gen I Graphene Super Batteries
The graphene super batteries (Gen I) are improved lithium-ion batteries that contain graphene.
The high electrical conductivity of graphene helps improve the electrochemical properties of the anode and the cathode of the batteries. This results in outstanding energy density, power density, and cycling life of this new generation of improved lithium-ion batteries with revolutionary energy storage abilities.
Graphene Super Batteries (Gen II)
The Graphene super batteries (Gen II) contain nanoscale materials with much better performance than the ones currently used for batteries on the market.
The nanostructured electrodes are key to the exceptionally high energy and power densities of the battery. The batteries also have a longer cycle life than typical lithium-ion batteries, making them an ideal candidate for portable electronic devices.
Applications in the Industry
The new graphene lithium batteries have an extensive range of applications. With phones and laptops being so largely used in people’s everyday lives, having a more reliable battery on a portable electronic device would significantly improve the electronics industry.
Electric Vehicle Batteries
The new revolutionary energy storage solutions will also find their applications in electric vehicle batteries. The biggest challenge faced by the electric vehicles industry is related to the batteries the vehicles use and the way they are charged.
On average, it can take 6-8 hours to fully charge an electric car using a slow charger or 20-40 minutes if using a fast charger. Since charging an electric vehicle is a lot more time consuming than refueling a normal car, electric vehicle users must often plan ahead and consider the type of charger available on their route or their parking space.
These limitations can be overcome with Nanotech Energy’s graphene-based super batteries, as charging times for electric vehicles could be reduced significantly.
Future Developments of Energy Storage Technology
With the wide use of portable electronic devices, the batteries industry's development becomes crucial for people’s everyday lives. The products that Nanotech Energy will bring to the market are expected to revolutionize energy storage, allowing a better lifecycle and faster charging.
The graphene lithium super batteries are an important step towards finding greener solutions to many environmental problems that society is facing in the 21st century.
References and Further Reading
Nobel Foundation (2019). Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2019: Lithium-ion batteries. [Online] Science Daily. Available at: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/10/191009082508.htm (Accessed on 28 October 2020).
Nanotech energy (2020). [Online] Nanotech energy. Available at: https://nanotechenergy.com/ (Accessed on 28 October 2020).
Geim, A. K. and Novoselov, K.S. (2007) The rise of graphene. Nature materials. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1849.
Byles, B. et al. (2016) The role of electronic and ionic conductivities in the rate performance of tunnel structured manganese oxides in Li-ion batteries. APL Materials. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948272.
Nobel Foundation (2019) Press release: The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2019 [Online] The Nobel Prize. Available at: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/2019/press-release/ (Accessed on 28 October 2020).
Ashkrof, P., et al. (2020) Analysis of the effect of charging needs on battery electric vehicle drivers’ route choice behaviour: A case study in the Netherlands. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2019.102206.
Emer, J.S. (2008) Foreword. Architecture Design for Soft Errors. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012369529-1.50001-X
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.