Apr 23 2009
Superconductivity is caused by electrons forming pairs in particular types of materials. This pairing makes the electrons insensitive to the perturbations in their pathway and leads to the disappearance of any electrical resistance. Although electron pairing is relatively well understood for conventional superconductors, many questions remain for the more unconventional class of high-temperature superconductors. Researchers from RIKEN's Advanced Science Institute in Wako, in collaboration with researchers from Rutgers University, US, and Kyoto University, have now developed an experimental method that enables the investigation of the electron pairing mechanism even for these more complex superconductors.
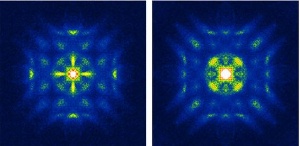 Scattering patterns of superconducting electron pairs revealed. The patterns depicting scattering mechanisms without vortices (left) appear markedly different to those in the presence of vortices (right), providing direct clues to the nature of the electron pairs.
Scattering patterns of superconducting electron pairs revealed. The patterns depicting scattering mechanisms without vortices (left) appear markedly different to those in the presence of vortices (right), providing direct clues to the nature of the electron pairs.
The experimentally measurable quantity that reflects the electron pairing in superconductors is governed by the so-called coherence factor—a measure of coordinated movement of the paired electrons. However, in the high-temperature superconductors the coherence factor is obscured by other effects and therefore impossible to measure with conventional techniques. “Our study establishes a new method to investigate the coherence factor in these complicated superconductors,” says Tetsuo Hanaguri from the research team.
The technique Hanaguri and colleagues developed, which is published in the journal Science*, is a scanning microscopy-based method that derives the coherence factor from the unique reaction of electron pairs to magnetic fields. The magnetic field enters the superconductor in the form of tiny bundles called vortices. In the center of a vortex, the superconducting state ceases to exist so that if the superconducting electron pairs encounter a vortex, the pairs get scattered. This type of scattering is different to that caused by other sources such as impurities in the sample.
To distinguish between these different scattering properties, the researches mapped the surface of a high-temperature superconductor. The comparison between scattering patterns with and without magnetic fields shows remarkable differences. These differences are unique signatures of the coherence factor and provide important clues on the symmetry properties of the electron pairs.
However, the impact of this technique extends beyond these results: it also offers an insight into the nature of electron pairs in other classes of unconventional superconductors. An example is the recently discovered class of iron-based superconductors, whose precise properties are under intense debate.
Furthermore, these experiments may enable the observation of other electronic phenomena that may exist in superconductors, says Hanaguri. “Different coherence factors may appear for other phenomena. By examining their influence on the coherence-factor we will be able to infer the presence of states which may compete or coexist with superconductivity.”
- Hanaguri, T., Kohsaka, Y., Ono, M., Maltseva, M., Coleman, P., Yamada, I., Azuma, M., Takano, M., Ohishi, K. & Takagi, H. Coherence factors in a high-Tc cuprate probed by quasi-particle scattering off vortices. Science 323, 923–926 (2009).