Oct 5 2009
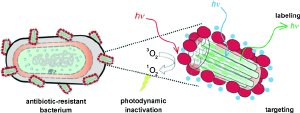
The increasing antibiotic resistance of bacteria is a serious problem of our time. Hospital germs in particular have developed strains against which practically every current antibiotic is ineffective. In the battle against resistant microbes, a team at the University of Münster (Germany) is now pursuing a new approach involving photodynamic therapy, which is a technique that is already being used in the treatment of certain forms of cancer and macular degeneration. Upon irradiation with light, an agent produces oxygen in a special activated form that is highly toxic to cells. As the researchers led by Cristian A. Strassert and Luisa De Cola report in the journal Angewandte Chemie, they would like to use specially developed nanomaterials that bind specifically to bacterial cells to mark them and kill them under irradiation.
 © Wiley-VCH
© Wiley-VCH
The researchers use nanoparticles made of a special porous material (zeolite L). The particles are modified so they carry a coating of amino groups. These bind preferentially to the surfaces of bacterial cells by means of electrostatic attraction and hydrogen bonds. The researchers put a green fluorescent dye into the channels of the mineral, making the bacteria visible under a fluorescence microscope. The actual “weapons” are photosensitizers anchored on the surface of the nanoparticles. When these molecules are irradiated with light of the right wavelength, they absorb the light energy and transfer it to oxygen molecules found in the surroundings, for example in infected tissue. The oxygen is excited and enters into what is known as the singlet state, in which it is highly reactive and attacks biomolecules – but only in the immediate area in which the singlet oxygen was generated. In this case, the location is right on the bacterial cell where the mineral particle is bound.
The scientists tested their new light-activated killer particles on antibiotic-resistant cultures of E. coli bacteria. After about two hours of irradiation, the bacteria were almost completely killed off. The team achieved comparable results with a strain of resistant gonococci. Furthermore, the researchers from Münster are also considering this material for the treatment of skin cancer. In this case, the tumor cells could be destroyed upon targeted irradiation with red light.