Nov 26 2009
In the fruit fly Drosophila, oskar mRNA, which is involved in defining the animal's body axes, is produced in the nuclei of nurse cells neighbouring the oocyte, and must be transported to the oocyte and along its entire length before being translated into protein.
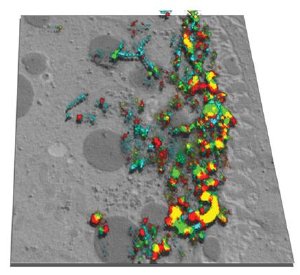 This electron microscopy image (grey) shows the posterior pole of a Drosophila oocyte, and superimposed on it is a projection of the movement of oskar mRNA in this region, recorded from a different oocyte at the same developmental stage. During this one-minute recording, the RNA moved from starting points labelled red to endpoints labelled green, via trajectories shown in blue. Image credit: Ephrussi/EMBL
This electron microscopy image (grey) shows the posterior pole of a Drosophila oocyte, and superimposed on it is a projection of the movement of oskar mRNA in this region, recorded from a different oocyte at the same developmental stage. During this one-minute recording, the RNA moved from starting points labelled red to endpoints labelled green, via trajectories shown in blue. Image credit: Ephrussi/EMBL
Scientists in the group of Anne Ephrussi at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have visualized the molecular mechanism that underlies this localisation process. In a study published today in Cell, they showed for the first time that, upon export from the nucleus of nurse cells into the cytosol – the semifluid that surrounds a cell’s nucleus –RNA particles recruit two motor proteins, kinesin and dynein, which transport the RNA to its final location in the oocyte.
By combining immunofluorescence with electron microscopy imaging, the EMBL scientists were able to discriminate where different molecules critical for oskar mRNA transport are recruited, thus defining a hierarchy of RNA particle assembly. These findings not only increase our understanding of development, but could also shed light on processes underlying the function of dendrites and axons in neurons, and synaptic plasticity – which is implicated in learning and memory formation – as these also entail the transport and localised translation of RNA.