Jun 2 2010
An organic molecule that has been found to be effective in making silicon-based electronics may be viable for building electronics on sheets of carbon only a single molecule thick. Researchers at the Max Plank Institute for Metals Research in Stuttgart report the advance in a paper appearing online in the journal Physical Review B on June 1.
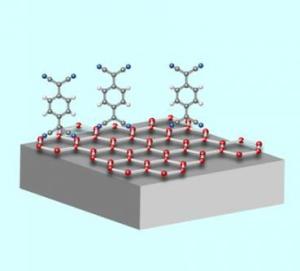 Dopant chemicals adhere to a graphene sheet, modifying its properties for the development of ultra small and fast electronic devices.
Dopant chemicals adhere to a graphene sheet, modifying its properties for the development of ultra small and fast electronic devices.
Ultrathin carbon layers known as graphene show promise as the basis for a host of extremely small and efficient electronic devices. But in order to create a useful component, the electronic properties of materials like silicon or graphene must be tailored through a doping process. Typically, silicon-based devices are doped by replacing some of the atoms in a silicon crystal with various dopant atoms or molecules . In graphene, on the other hand, dopants are generally deposited on top of the carbon sheet rather than taking the place of some of the carbon atoms. Materials such as gold, bismuth and nitrogen dioxide have been used to dope graphene with varying degrees of success. Now, Max Planck Institute researchers have found that the compound F4-TCNQ (tetrafluoro-tetracyanoquinodimethane), which has been proven effective for producing LEDs in silicon, seems to fit the bill for graphene as well. F4-TCNQ forms stable layers on graphene that are fairly robust under exposure to elevated levels of heat and light, and can control graphene electrical properties in ways that suggest it may be a good dopant choice.
In a Viewpoint article in the current issue of APS Physics, Alexei Fedorov of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory describes the challenges of creating electronic devices built of graphene and recent attempts to identify doping materials to do the job.
Source: http://www.aps.org/