Researchers at the Norwegian Radium Hospital’s Centre of Cancer Biomedicine have demonstrated that the introduction and storing of nanoparticles within cells will have a detrimental effect on the transportation of critical substances into and out of the cells, resulting in unwanted changes in the physiology of the cells and their functioning.
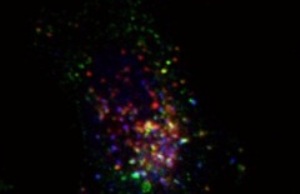 This photo shows uptake of fluorescent nanoparticles inside cells. The yellow and violet dots are particles that have been transported into the cell and have accumulated. (Photo: Radiumhospitalet)
This photo shows uptake of fluorescent nanoparticles inside cells. The yellow and violet dots are particles that have been transported into the cell and have accumulated. (Photo: Radiumhospitalet)
A team of researchers led by Tore-Geir Iversen has discovered the behavior of nanoparticles in cells. It has investigated nanoparticles that have a diameter of 30-100 nm, the standard size utilized for delivering DNA and drugs into cells. The team dyed the nanoparticles in order to illuminate them during irradiation by a laser. The scientists were able to spot the different nanoparticles inside the cells utilizing a microscope, by dyeing the particles with a range of fluorescent substances and subjecting them to irradiation with different laser wavelengths.
During the study, the researchers observed that a nanoparticle-bound protein stays inside the cell and piles up in the endosomes, which perform critical function in the internal transport system of a cell. The accumulated nanoparticles then interrupted the transportation of critical elements in and out of a cell. This finding is vital in developing future nanoparticles.
The Norwegian Radium Hospital scientists’ next step is to determine whether nanoparticles with diameters below 30 nm will handle the transport system in a better way. Moreover, in partnership with materials scientists, they want to develop nanoparticles with specific surface compositions and sizes that enable the particles to stably travel in the blood stream and react particularly with the target cells but assure the particles can be broken down inside the cells. The cell biologists will also partner with immunologists prior to starting animal trials.