Researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich have developed a new method of using nanotubes to detect molecules at extremely low concentrations enabling trace detection of biological threats, explosives and drugs.
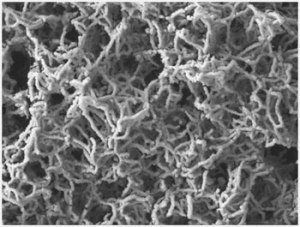 The top view of the jungle canopy (zoom in for best case: hafnium thickness of 2.5nanometers and gold thickness of 20 nanometers
The top view of the jungle canopy (zoom in for best case: hafnium thickness of 2.5nanometers and gold thickness of 20 nanometers
The joint research team, led by LLNL Engineer Tiziana Bond and ETH Scientist Hyung Gyu Park, are using spaghetti-like, gold-hafnium-coated carbon nanotubes (CNT) to amplify the detection capabilities in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).
SERS is a surface-sensitive technique that enhances the inelastic scattering of photons by molecules adsorbed on rough metal surfaces or by nanostructures.
Bond and her collaborators are using metal-coated nanotubes bunched together like a jungle canopy to amplify the signals of both the incident and Raman scattered light by exciting local electron plasmons.
Their real breakthrough, however, is discovering the use of an intermediate dielectric coating (hafnium) to block the quenching of the free electrons in the metal by the CNTs, allowing the nanotubes to function uninhibited.
By preserving the electrons and enhancing the light through the use of nanotube jungles, the team is able to significantly increase the SERS' detection sensitivities in CNTs structures.
The hafnium coating enables the bunching of gold nanotubes that creates a thick canopy full of sensitive spots for detection. The nanotubes enable incident light to be trapped and focused at the numerous contact points and crevices, allowing the Raman-scattered light to pass through. This enables portable Raman devices to detect and identify specific airborne substances randomly.
"This is a very important discovery in our efforts to improve the use of SERS devices," Bond said. "We gained this valuable knowledge through multidisciplinary basic research and approaching the problem with a rational design."
Bond and Park hope their engineered material will eventually be used in portable devices to conduct on-site analysis of chemical impurities such as environmental pollutants or pharmaceutical residues in water. Other applications include the real-time point-of-care monitoring of physiological levels for the biomedical industry and fast screening of drugs and toxins for law enforcement.
"We are in the process of filing a patent for our new discovery," Bond said.
Bond and Park's discovery was recently featured on the cover of the issue of Advanced Materials.