Sep 13 2016
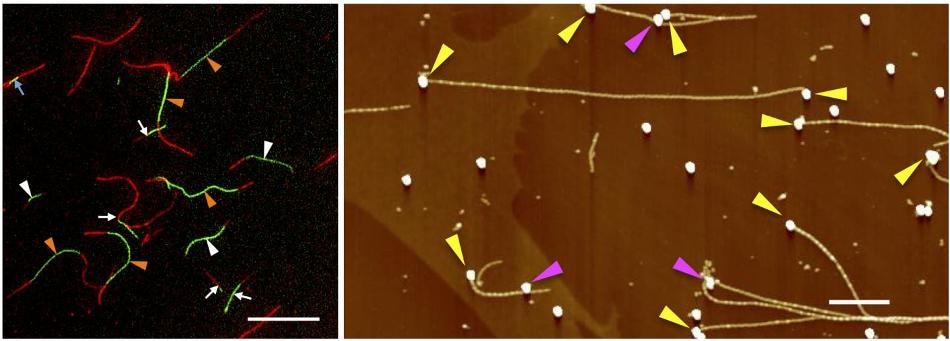 (Left) Growth of tandem fluorescent fibrils is shown. Scale bar = 20 micrometers. (Right) Fibrils extended from gold nanoparticles placed on the surface of a substrate. Scale bar = 1 micrometer. (CREDIT: Hokkaido University)
(Left) Growth of tandem fluorescent fibrils is shown. Scale bar = 20 micrometers. (Right) Fibrils extended from gold nanoparticles placed on the surface of a substrate. Scale bar = 1 micrometer. (CREDIT: Hokkaido University)
A versatile method to pattern the structure of nanowires has been developed by a team of Hokkaido University researchers. This new method provides a tool that will aid the development of novel nanodevices.
Many researchers across the world have shown considerable interest in the patterning of functionalized nanowires, due to the advantageous applications of these materials in nanodevice construction, and because they are excellent catalyzers and possess good semiconductivity .
A versatile approach to make functionalized nanowires with specific need to control spatial patterning is considered essential.
Previously, a team of researchers headed by Professor Kazuyasu Sakaguchi of the Faculty of Science’s Department of Chemistry, developed an effective method known as structure-controllable amyloid peptides (SCAPs) in order to monitor the self-assembly of amyloid peptides, which act as building blocks of nanowires and also known as the causative molecule for Alzheimer’s disease.
In the latest research, the researchers integrated the SCAPs with templated fibril growth (a unique property of amyloid peptides) and successfully formed nanowires with tandem domain structures or just one nanowire extending from a particular starting point.
In order to form the tandem structure, researchers used the SCAPs method to develop the initial amyloid fibrils that were marked by green fluorescence and also used as a template. It was also used to allow another type of amyloid peptide that was marked by red fluorescence that extended from the starting fibrils.
The study shows 67% tandem yield - three times higher than the efficiency yield of earlier studies. Some of the geometrical patterns could be detected in the tandem structures, the proportion of which could also be monitored by altering the peptide mix ratio.
Researchers were successful in developing a single nanowire in a particular location by fixing template fibrils to gold nanoparticles kept on substrate surface using molecular recognition and then permitting new fibrils to extend from the template. This is globally considered to be the very first time that researchers have successfully obtained this type of advanced pattern control.
This method can be ideally applied for self-assembly of nanowires for nanoelectrodes that are developed using lithography.
It could also be used to prepare a wide variety of fibril patterns and hence open up new avenues for the development of novel self-assembled nanodevices.
Professor Kazuyasu Sakaguchi, Hokkaido University