According to a recent review published by Prof. Changyang Gong’s research team at Sichuan University’s Department of Biotherapy, Cancer Center, and State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, the rapid development of nanoparticles as delivery systems holds great promise for advancing therapeutic approaches for the treatment of cancer.
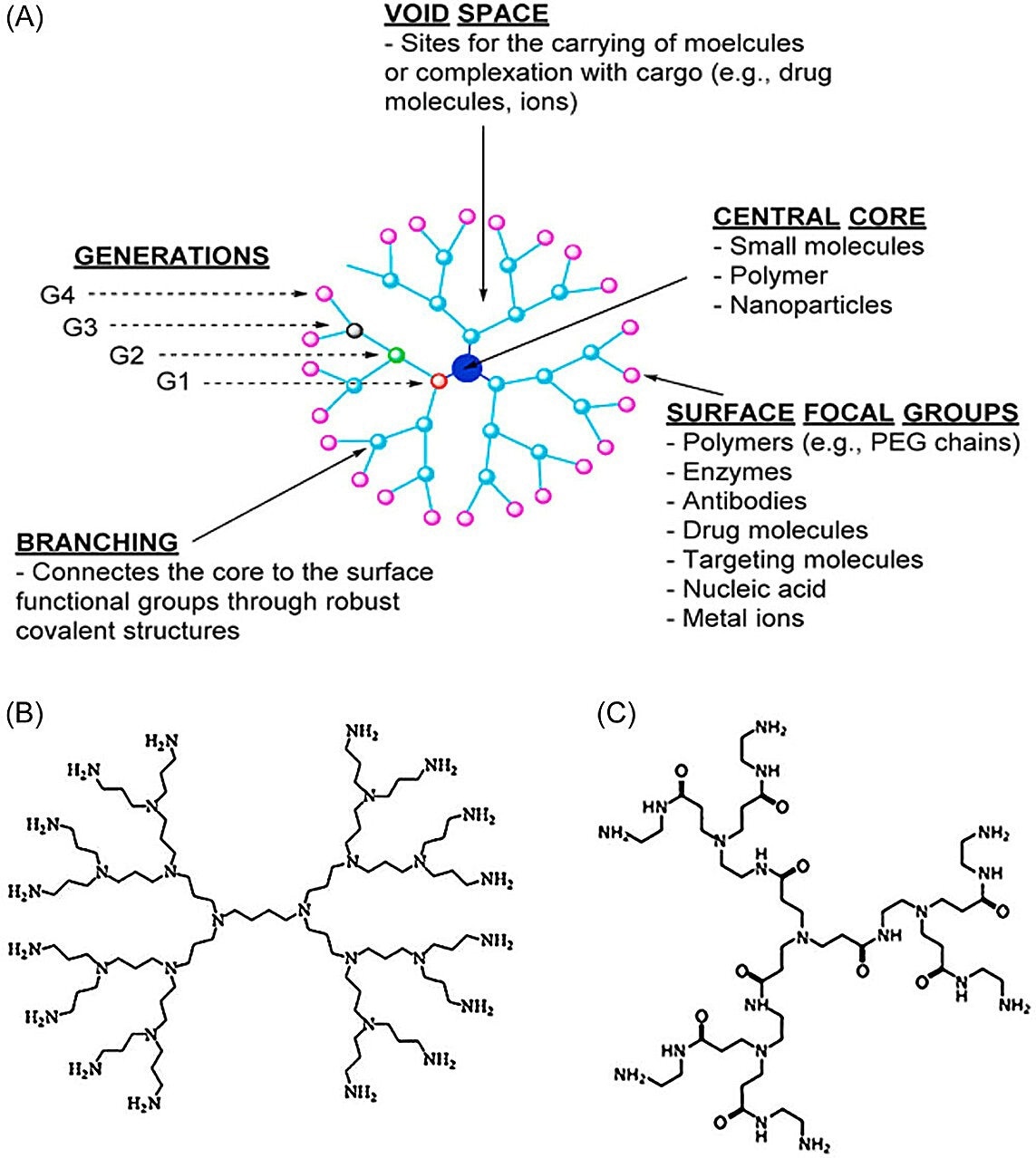 Typical structures of dendrimer NPs. (A) The typical structures of dendrimers are central core, generations, void space, branching, and surface focal groups. Copyright Permission from Chowdhury et al. (B) Poly(propyleneimine) dendrimers. Copyright Permission from Sherje et al. (C) Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers. Image Credit: MedComm – Oncology (2024). DOI: 10.1002/mog2.67
Typical structures of dendrimer NPs. (A) The typical structures of dendrimers are central core, generations, void space, branching, and surface focal groups. Copyright Permission from Chowdhury et al. (B) Poly(propyleneimine) dendrimers. Copyright Permission from Sherje et al. (C) Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers. Image Credit: MedComm – Oncology (2024). DOI: 10.1002/mog2.67
MedComm-Oncology journal published the study.
Currently, a wide variety of nanoparticles with distinct characteristics are being created. Micelles, liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, dendrimer nanoparticles, polymersomes, protein nanoparticles, inorganic nanoparticles, exosomes, biomimetic nanoparticles, molecularly imprinted nanoparticles, and hybrid nanoparticles are a few examples of the nanoparticles used in cancer therapy.
Even though cancer is a complicated disease, treating it presents a variety of challenges. Thankfully, scientists have created nanoparticles to overcome various obstacles and produce complex delivery systems to improve a range of treatments.
These methods ensure the delivery and functionality of loaded drugs. Nanotechnology’s versatility and modifiability allow cargoes to have long-circulation times, targeting abilities, and responsiveness to pH, redox, GSH, enzymes, hypoxia, ATP, temperature, and ions, as well as securing cargoes to their destined subcellar localizations.
Cancer treatment has made extensive use of these potent nanotechnologies. With the use of nanoparticles, remarkable progress has been made in cancer treatment. Applications include combination therapy and single therapies, such as phototherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapy.
A cooperative nano-CRISPR scaffold (Nano-CD) is an excellent example. By activating the caspase-3 pathway and GSDME expression, Nano-CD has co-delivered cisplatin and CRISPR/dCas9 plasmid to synthesize GSDME protein, which specifically induces significant pyroptosis in tumor cells.
Researchers are swiftly gaining a more profound comprehension of the obstacles and possibilities presented by various nanoparticles for cancer treatment. The most recent developments in nanoparticle technology have been discussed in this study to overcome these issues and, on the other hand, provide additional innovative possibilities.
Researchers anticipate that these advancements and the tireless work of researchers in the area will further support nanoparticles’ attempts to change the paradigm of cancer therapy and establish nanoparticle-associated cancer therapies as standard therapeutic procedures.
Journal Reference:
Huang, X., et. al. (2024) Advances and applications of nanoparticles in cancer therapy. MedComm-Oncology. doi:10.1002/mog2.67